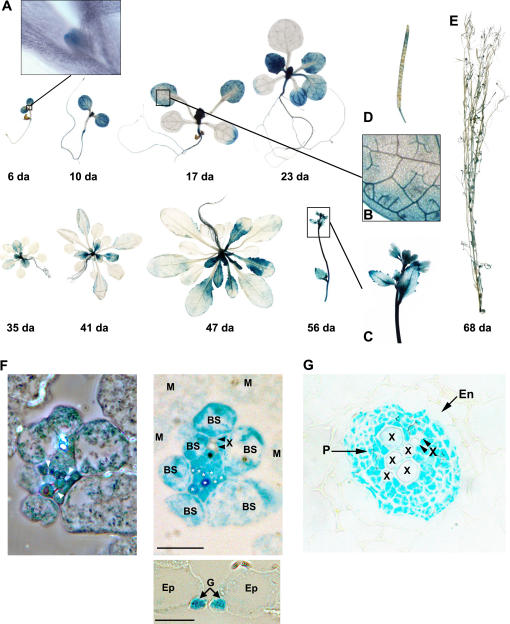
Figure 6.
The expression of AtNSI is developmentally regulated in Arabidopsis. Whole-mount (A–E) or thick (F and G) sections from X-glucA-stained transgenic Arabidopsis lines expressing the NSI promoter-GUS fusion pC1301-PAtNSI∷GUS. A, Examination of transgenic lines from 6 through 56 d post germination shows that expression of the NSI promoter is restricted to young tissues and resembles the sink-to-source transition. Inset shows a high magnification image of the shoot apical meristem from a 6-d-old plant exhibiting a high level of pC1301-PAtNSI∷GUS expression. B, High magnification image of rosette leaf from a 17-d-old transgenic plant. The NSI promoter, based on X-glucA staining, is strongly expressed in veins, with all vein orders appearing to be equally stained. C, Developing inflorescence from a 56-d-old transgenic plant. D, Silique from 68-d-old transgenic plant showing developmental regulation of NSI promoter expression in maturing siliques. GUS expression is high in immature siliques and decreases as the siliques mature, becoming undetectable in mature siliques. F, Two-micron transverse sections of a GUS-stained rosette leaf from 2-week-old transgenic plants. Phase-contrast (left) and Nomarski (right) images of adjoining transverse sections of the same minor vein are shown. Strong GUS staining appears to be uniform throughout the vascular tissue in both phloem companion cells (indicated by asterisks) and xylem parenchyma cells. Phloem companion cells are clearly identified in the phase contrast image as flanking the sieve elements (arrows) and appear very heavily stained. X, Xylem; BS, bundle sheath cell; M, mesophyll cell. Inset, Nomarski image of transverse section from rosette leaf showing strong and specific GUS staining in guard cells. G, Guard cell; Ep, epidermal cell. G, Two-micron transverse section of primary root from 2-week-old transgenic plant showing the stele. GUS staining appears to be uniform and strong throughout the vascular tissue. Note very sharp boundary between the phloem tissue (stele) and endodermal layer. P, Phloem; X, xylem; En, endoderm. Scale bars in F (right and inset) are 20 μm.