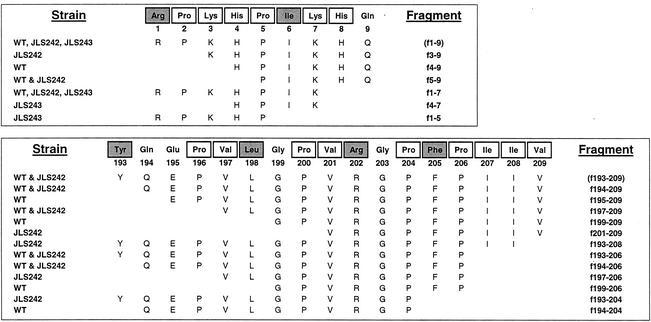
FIG. 1.
Peptide sequences of αS1-CN(f1-9) and β-CN(f193-209) and fragments derived from hydrolysis with CFEs. The residues that are enclosed in boxes are essential amino acids for L. helveticus. The shaded residues are essential amino acids that occur only once in the peptide and therefore must be liberated for growth of L. helveticus when the peptide is supplied as the sole substrate. The peptides correspond to unique values obtained for RP-HPLC fractions from mass spectrometry data. The strain column indicates from which CFE reaction(s) a given peptide was identified. The peptide profile obtained from hydrolysis of αS1-CN(f1-9) by CFE from the wild type (WT) is also representative of the results of the reactions with the ΔpepC, ΔpepO, and ΔpepE strains. Similarly, the peptide profile obtained from hydrolysis of β-CN(f193-209) by CFE from the wild type is also representative of the results of the reactions with the ΔpepC, ΔpepO, ΔpepE, and ΔpepX strains.