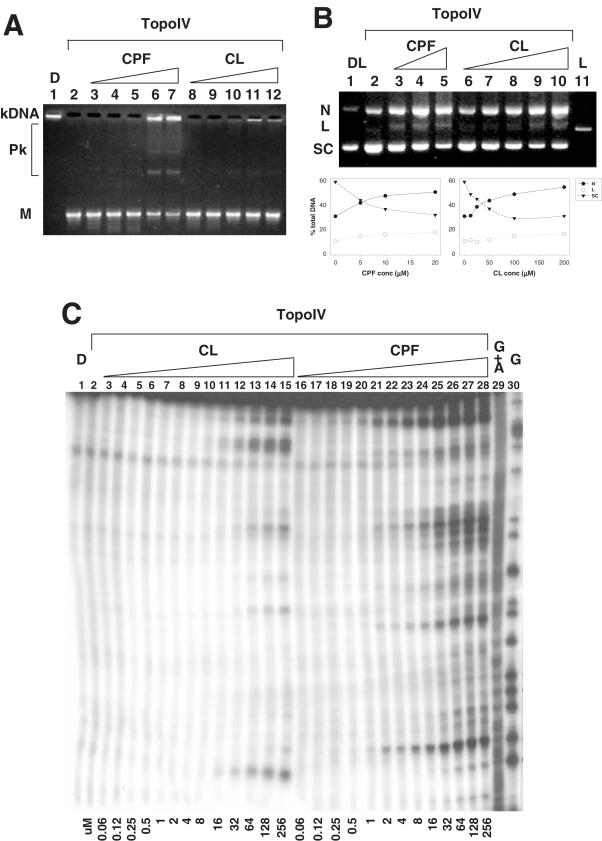
Figure 2.
CL poisons topoisomerase IV. (A) Inhibition of the decatenation activity of the enzyme. Kinetoplast DNA (kDNA) was incubated with topoisomerase IV and increasing amounts (12.5, 25, 50, 100, 200 µM) of CPF, (lanes 3–7) or CL (lanes 8–12). Reaction mixtures were loaded and run on a 1% agarose gel. DNA bands were visualized with ethidium bromide staining. Lane 2 is a control for topoisomerase enzymatic activity in the absence of the drugs and lane 1 is a control for the input kDNA. M denotes released minicircle DNA. Pk indicates partially catenated DNA intermediates. (B and C) Stimulation of enzyme-mediated DNA breaks. (B) Supercoiled plasmid pBR322 was incubated with increasing amounts of CPF (5, 10, 20 µM, lanes 3–5) or CL (12.5, 25, 50, 100, 200 µM, lanes 6–10) and loaded on a 1% agarose gel. DNA bands were visualized with ethidium bromide staining. Lane 2 is a control for the cleavage activity of topoisomerase IV without drugs. Lane 1 shows the input supercoiled plasmid DNA and lane 11 is a control for linear plasmid DNA. Band identities are shown on the left. N, L and SC indicate nicked, linear and supercoiled plasmid DNA, respectively. For any given DNA sample, the percentage of nicked, linear and supercoiled DNA bands were determined by dividing the relevant band intensity by the total DNA intensity loaded into that particular track. Quantification data are shown below the gel figure. (C) A 239 bp SV40 DNA fragment, labelled with 32P at one 5′ end, was incubated with topoisomerase IV and increasing amounts (60 nM–256 µM) of CL (lanes 3–15) or CPF (lanes 16–28). Reaction mixtures were loaded and run on a denaturing urea-8% polyacrylamide gel. DNA fragments were visualized by phosphorimaging. Lane 1 and 2 are controls for non-treated DNA and DNA incubated with the enzyme without drugs. Lane 29 and 30 are respective G+A and G sequencing products obtained according to the Maxam and Gilbert protocol (23). Drug concentrations present in cleavage reactions are shown at the bottom of the gel.