Figure 4.
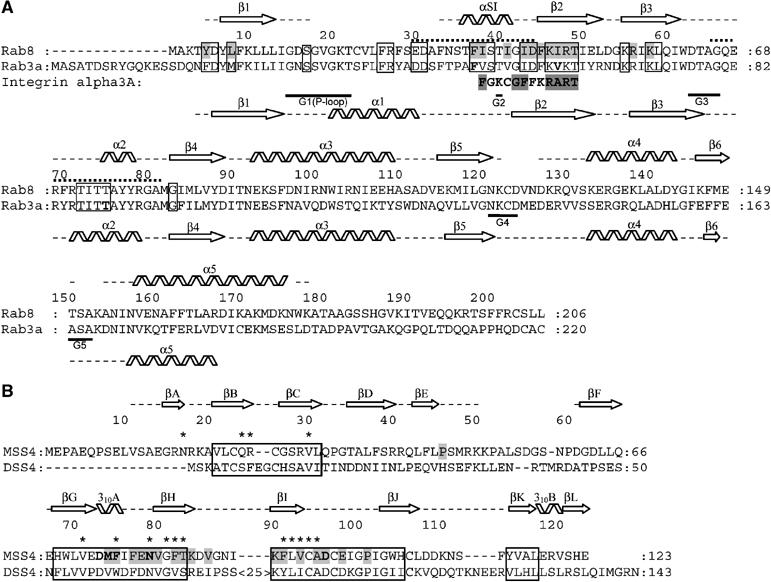
(A) Structure-based sequence alignment of Rab3a and Rab8. Secondary structure element distribution is shown and labeled for Rab3 and Rab8 at the bottom and at the top, respectively. Gaps in the secondary structure assignment correspond to structurally undefined regions. Dotted lines indicate the Switch I and Switch II regions. Guanine nucleotide-binding regions G1–G5 are labeled. Exocytic Rab conserved regions are boxed (see Supplementary Figure S1). Residues in Rab3 shown by mutational analysis to be important for MSS4-binding and nucleotide-release activity (Zhu et al, 2001a) are shown in bold. Residues in Rab8 involved in direct interactions with MSS4 are highlighted in gray. The integrin alpha 3a-derived peptide identified as a binding partner of MSS4 is also aligned to the Rab sequences. (B) Structure-based sequence alignment of human MSS4 and DSS4 proteins. MSS4/DSS4 conserved regions (Zhu et al, 2001b) are boxed. Residues in MSS4 shown by mutational analysis to be important for Rab-binding and nucleotide-release activity are shown in bold, residues involved in direct interactions with Rab8 are highlighted in gray. Residues in DSS4 that undergo chemical shift perturbations in the presence of Sec4 are marked with asterisks (Yu and Schreiber, 1995b).
