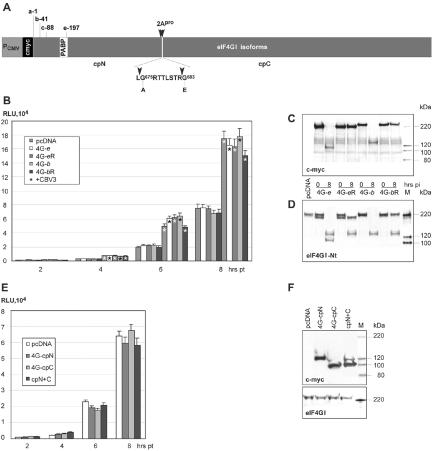
FIG. 7.
Effect of eIF4GI overexpression on EV IRES-mediated translation. (A) eIF4GI expression construct structure; an N-terminal c-myc tag (black box) is fused to the eIF4GI ORF at authentic initiation codons b and e (9, 11). PABP binding (white box) and EV 2Apro cleavage sites (arrowheads) are indicated. The 2Apro-induced N-terminal and C-terminal cleavage products are designated cpN and cpC, respectively. Two amino acids, Gly683 and Gly675 (56), were mutated to generate 2Apro-resistant eIF4GI variants. (B) rLuc translation in HeLa cells transiently expressing exogenous eIF4GI isoforms and their cleavage-resistant variants. (C) Expression of c-myc-tagged eIF4GI isoforms in HeLa cells at 0 and 8 hpi with CBV3. The integrity of exogenous eIF4GI was determined by Western blotting with α-c-myc. (D) Expression levels and integrity of total cellular eIF4GI were determined by Western blotting with α-eIF4GI-Nt. (E) CBV3 IRES-driven rLuc translation in HeLa cells expressing eIF4GI cleavage products. (F) Expression levels of eIF4GI proteolytic cleavage products and endogenous eIF4GI.