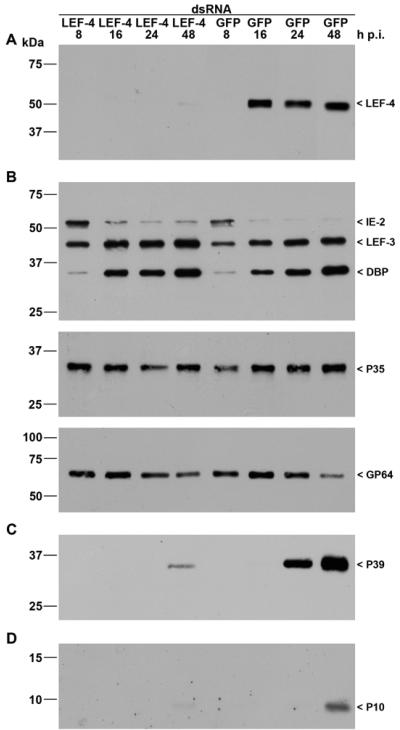
FIG. 2.
Inhibition of viral gene expression by lef-4 silencing. S. frugiperda cells were transfected with either LEF-4 or GFP dsRNA. Cells were subsequently infected with AcMNPV (10 PFU/cell) at 20 h posttransfection, and detergent-based nuclear and cytoplasmic extracts were prepared from infected cells 8, 16, 24, and 48 h p.i. Proteins were resolved on sodium dodecyl sulfate-10% polyacrylamide gels and transferred to nitrocellulose membranes (A, B, and C) or resolved on sodium dodecyl sulfate-15% polyacrylamide gels and transferred to polyvinylidene difluoride membranes (D). (A) LEF-4 was stained with rabbit anti-Lef-4 antiserum. (B) Early gene expression was analyzed with rabbit antisera raised against IE2 (16), LEF-3 (3), DBP (22), or P35 (11) or with mouse monoclonal anti-GP64 (AcV5) (12). (C) Late gene expression was analyzed with mouse monoclonal anti-P39 (P10C6) (30). (D) Expression of the very late protein P10 was detectable with rabbit anti-P10 serum (29). Expression of LEF-4, IE2, LEF-3, DBP, P39, and P10 was analyzed on samples of nuclear protein fractions, and P35 and GP64 expression was detected in cytoplasmic fractions as described previously (21). Protein size markers are shown on the left, and the identities of the viral proteins are indicated on the right.