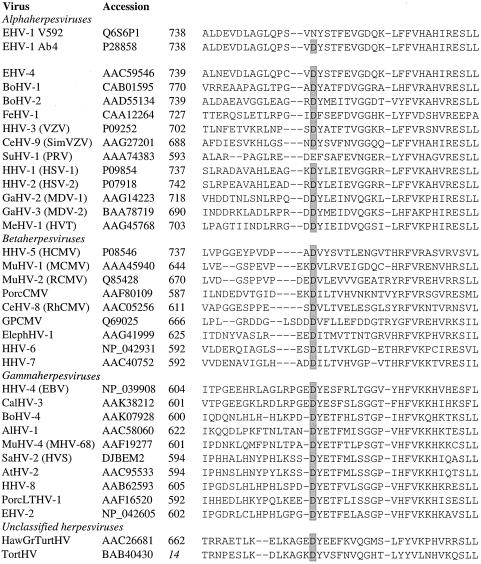
FIG. 3.
An alignment of amino acid sequences for various herpesvirus DNA polymerases is shown, generated using ClustalW (run using the BioEdit software [21]). For each sequence, the name of the virus, database accession number, and residue number of the first amino acid are shown (the residue number in italics refers to a partial polymerase sequence). The conserved aspartate residue, corresponding to D/N752 of the EHV-1 polymerase, is highlighted by gray shading. BoHV-1, bovine herpesvirus 1; FeHV-1, felid herpesvirus 1; HHV-3, human herpesvirus 3; CeHV-9, cercopithecine herpesvirus 9; SimVZV, simian VZV; SuHV-1, suid herpesvirus 1; PRV, pseudorabies virus; GaHV-2, gallid herpesvirus 2; MDV-1, Marek's disease virus type 1; MeHV-1, meleagrid herpesvirus 1; HVT, herpesvirus of turkeys; MuHV-1, murid herpesvirus 1; MCMV, mouse cytomegalovirus; RCMV, rat cytomegalovirus; PorcCMV, porcine cytomegalovirus; RhCMV, rhesus monkey cytomegalovirus; GPCMV, guinea pig cytomegalovirus; ElephHV-1, elephantid herpesvirus 1; EBV, Epstein-Barr virus; CalHV-3, callitrichine herpesvirus 3; AlHV-1, alcelaphine herpesvirus 1; MHV-68, mouse herpesvirus strain 68; SaHV-2, saimiriine herpesvirus 2; HVS, herpesvirus saimiri; AtHV-2, ateline herpesvirus 2; PorcLTHV-1, porcine lymphotropic herpesvirus 1; EHV-2, equine herpesvirus 2; HawGrTurtHV, Hawaiian green turtle herpesvirus; and TortHV, tortoise herpesvirus.