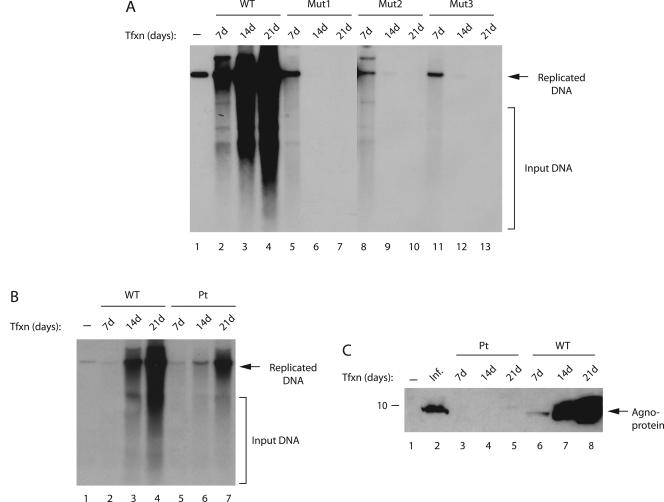
FIG. 3.
Replication properties of agnoprotein phosphorylation and point mutants. (A) Effect of agnoprotein phosphorylation mutants on viral replication. SVG-A cells were transfected with either Mad-1 WT genome or its agnoprotein mutant genomes (Mut1, Mut2, and Mut3) (8 μg/2 × 106 cells/75-cm2 flask) using Lipofectin as described in Materials and Methods. At 7, 14, and 21 days posttransfection, low-molecular-weight DNA was isolated by using a QIAGEN spin column (46), digested with BamHI and DpnI enzymes, resolved on a 1% agarose gel, and analyzed by Southern blotting. (B) Replication efficiency of an agnoprotein point mutant (Pt) virus compared to WT. SVG-A cells were transfected with either WT or Pt mutant virus, and replicated DNA was analyzed by a DpnI assay as described for panel A. In lane 1 in each panel, Mad-1 WT genome (2 ng) digested with BamHI was loaded as a positive control. Representative data are shown here. Input DNA (transfected) is indicated by a bracket, and replicated DNA is indicated by an arrow. (C) In parallel to the studies described for panel B, whole-cell lysates were also prepared at the indicated time points and analyzed by Western blotting with an anti-agnoprotein antibody. In lane 1, whole-cell extract from untransfected cells was loaded as a negative control. In lane 2, whole-cell extract from infected cells was loaded as a positive control. Tfxn, transfection; Inf, infection. The migration pattern of a molecular mass marker is shown on the left side of the panel in kilodaltons.