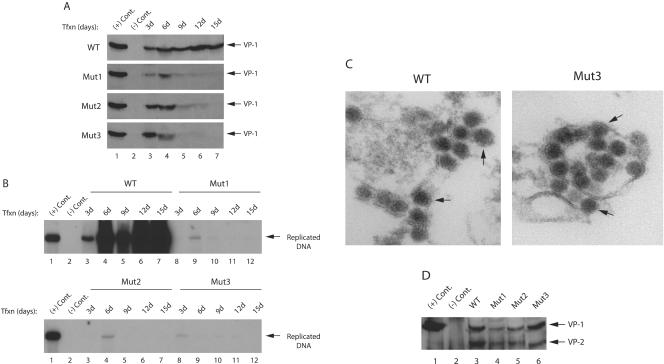
FIG. 6.
Analysis of virus release for phosphorylation mutants of agnoprotein. (A) Mad-1 WT genome or its agnoprotein phosphorylation mutants (Mut1, Mut2, and Mut3) were separately transfected into SVG-A cells (8 μg of DNA/2 × 106 cells/75-cm2 flask). Whole media (12 ml) were collected at the indicated time points, spun at 10,000 rpm to clear cell debris, and subjected to immunoprecipitation with an anti-VP1 antibody (10 μg). Half of the samples were analyzed by Western blotting with anti-VP1 antibody. The other half were analyzed by Southern blotting to detect encapsidated viral DNA. In lane 1, nuclear extract, prepared from infected cells, was loaded as a positive control [(+) Cont.]. In lane 2, nuclear extract, prepared from uninfected SVG-A cells, was loaded as a negative control [(−) Cont.)]. (B) Analysis of encapsidated viral DNA by Southern blotting. Encapsidated viral DNA from the released viral particles was purified by using QIAGEN spin columns (46), digested with BamHI and DpnI enzymes, resolved on 1% agarose gel, and analyzed by Southern blotting with probes prepared from whole Mad-1 genome. In lane 1, Mad-1 WT genome (2 ng) digested with BamHI was loaded as a positive control [(+) Cont.]. In lane 2, DNA isolated from untransfected cells was loaded as a negative control [(−) Cont.]. (C) Analysis of released viral particles by EM. Mad-1 WT genome or its agnoprotein mutant (Mut3) were separately transfected into SVG-A cells (8 μg of DNA/2 × 106 cells/75-cm2 flask). Released viral particles were immunoprecipitated by using an anti-VP-1 (pAB597) antibody on day 6 posttransfection and analyzed by EM. Arrows in both panels point to the JCV particles. (D) Mad-1 WT genome or its agnoprotein phosphorylation mutants (Mut1, Mut2, and Mut3) were separately transfected into SVG-A cells (8 μg of DNA/2 × 106 cells/75-cm2 flask). The released viral particles were immunoprecipitated by an anti-VP-1 antibody (pAB597) and analyzed by Western blotting with an antibody (a rabbit polyclonal antibody raised against SV40 capsid proteins, which is also cross-reactive with JCV viral capsid proteins) that detects viral capsid proteins. In lane 1, nuclear extract, prepared from infected cells, was loaded as a positive control [(+) Cont.]. In lane 2, nuclear extract, prepared from uninfected SVG-A cells, was loaded as a negative control [(−) Cont.].