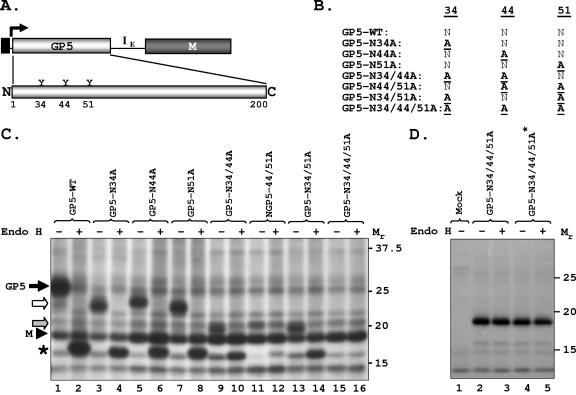
FIG. 2.
Glycosylation analysis of wt GP5 and its mutants in transfected cells. (A) Schematic of the bicistronic vector and PRRSV GP5 with the three putative glycosylation sites at amino acid positions 34, 44, and 51 shown. (B) Various mutants used in the present study. (C) Expression of wt and mutant GP5 and their sensitivity to Endo H. The experiment was performed as described in the legend to Fig. 1; proteins were immunoprecipitated with anti-GP5 antibody, digested with Endo H (+) or left undigested (−), and analyzed by electrophoresis. Mutant GP5 proteins are shown by open and shaded arrows. The protein band (∼17 kDa) identified by the asterisk is generated by Endo H digestion of the wt and mutant GP5 proteins. (D) Expression of the triple mutant GP5 N34/44/51A from plasmids with and without M. Cells were mock transfected (lane 1) or transfected with plasmids encoding the triple mutant-containing M coding region (GP5-N34/44/51A, lanes 2 and 3) or without the M coding region (GP5-N34/44/51A*, lanes 4 and 5). Proteins were radiolabeled and detected with anti-GP5 antibody as described above. The mobility of proteins is shown in kilodaltons on the right.