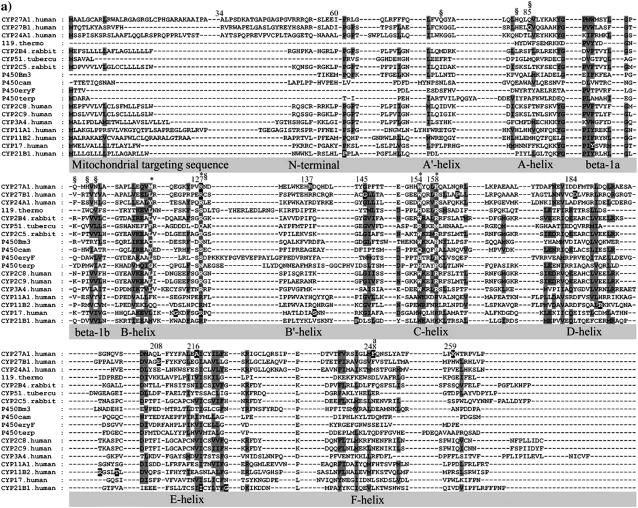
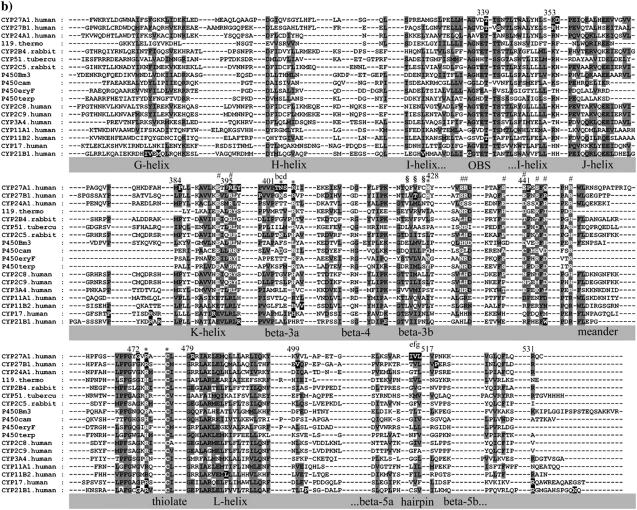
FIGURE 1.
Multisequence alignment of CYP27A1, CYP27B1, CYP24A1, CYP11A1, CYP11B2, CYP17, and CYP21B1. Primary sequences were parsed and secondary structure predictions assigned using the observed secondary structure and conserved hydrogen bonding patterns seen in eleven CYP crystallographic templates. Shaded positions with dark text denote similar residues conserved in at least 9 of 18 aligned sequences. Shaded positions with white text and marked with “*” and “#” denote heme-binding and ERR-triad residues, respectively. Residues in the β-sheets structurally positioned toward substrate recognition in a pw2a access channel are denoted by “§”. Residues mutated in this study are indicated with white text on black and identified by lower case letters: a, Phe-248-Met; b, Thr-402-Phe; c, Asn-403-Thr; d, Ser-404-Ala, Ser-404-Thr; e, Ile-514-Phe; f, Val-515-Ile, Val-515-Leu; and g, Leu-516-Val. Sites of missense mutations causing cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis (CYP27A1), vitamin D-dependency rickets (CYP27B1), and autosomal deficiencies in CYP11B1, CYP17, and CYP21B1 are also indicated with white text on black shading. Gaps within secondary structures were added to emphasize structurally important landmarks.