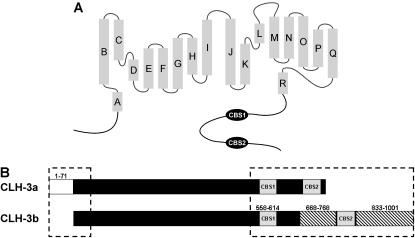
FIGURE 1.
ClC anion channel structural features. (A) Schematic diagram showing basic structural components of eukaryotic ClC anion channels. Shaded rectangles represent α helices (A–R) identified by x-ray crystallography of a bacterial ClC (5). The cytoplasmic C-terminus of eukaryotic ClCs contains two conserved cystathionine-β-synthase domains (CBS1 and CBS2). (B) Schematic diagram showing the major differences between the cytoplasmic N- and C-termini (dashed boxes) of CLH-3a and CLH-3b. Major differences between CLH-3a and CLH-3b include a 71 amino acid addition to the N-terminus of CLH-3a (amino acids 1–71), a 101 amino acid insertion between CBS1 and CBS2 in CLH-3b (amino acids 668–768), and a 169 amino acid extension of the CLH-3b C-terminus (amino acids 833–1001).