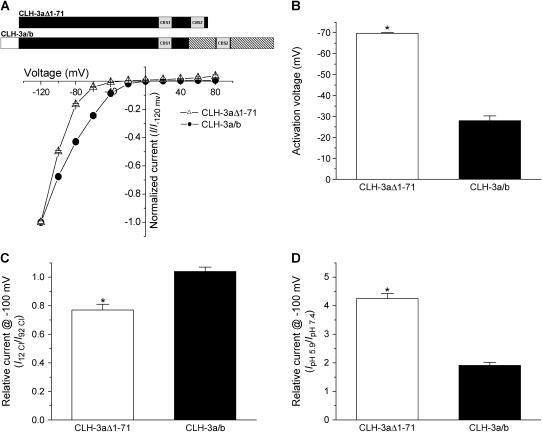
FIGURE 5.
Voltage, Cl−, and H+ sensitivity of CLH-3aΔ1-71 and CLH-3a/b. (A, B) I-V relationships and activation voltages. Voltage clamp protocol is the same as that described in the Fig. 3 A legend. I-V plots are normalized to the steady-state current measured at −120 mV. Values are means ± SE (n = 8–9). *p < 0.0001 compared to CLH-3a/b. A schematic diagram of the CLH-3aΔ1-71 and CLH-3a/b mutant channels is shown above the I-V plots. (C) Effect of reducing bath Cl− concentration from 92 mM to 12 mM on whole cell current amplitude measured at −100 mV. Current amplitude was normalized to that measured at 92 mM Cl− (I92 Cl). Values are means ± SE (n = 4–5). *p < 0.0001 compared to CLH-3a/b. Relative current for CLH-3a/b is not significantly different from 1 (p > 0.3). (D) Effect of bath pH on whole cell current amplitude measured at −100 mV. Current amplitude was normalized to that measured at pH 7.4 (IpH 7.4). Values are means ± SE (n = 8–9). *p < 0.0001 compared to CLH-3a/b. CLH-3aΔ1–71 requires stronger hyperpolarization for activation compared to CLH-3a/b. In addition, CLH-3aΔ1-71 is more sensitive to extracellular H+ and is inhibited by reducing bath Cl− concentration.