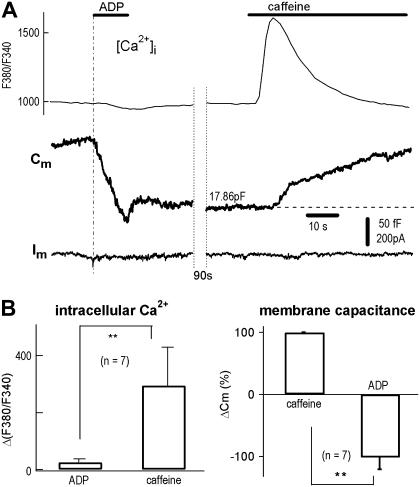
FIGURE 2.
ADP-induced endocytosis in the absence of Ca2+ influx and Ca2+ release from Ca2+ stores. (A) With the micro-puffer system for chemical stimulation and Cm recording for exocytosis (Cm increase) and endocytosis (Cm decrease), 0.1 mM ADP induced a rapid endocytosis (−116 fF). Subsequently, 20 mM caffeine induced an exocytosis (+83 fF). Combined [Ca2+]i imaging showed that caffeine, but not ADP, induced a [Ca2+]i spike (upper traces). Note, because the dilution in puffer tip (34), Cm reduction signal did not reach its saturation level during the 10 s application. (B) Statistics of experiments using protocols of panel A. [Ca2+]i measured by changes in F380/F340 (ΔF380/F340) was −25 ± 11 and 290 ± 110 (arbitrary units), corresponding to ADP and caffeine, respectively (left panel). ADP-induced endocytosis (decrease in Cm) was −102 ± 19% of caffeine-induced exocytosis (n = 7, right panel).