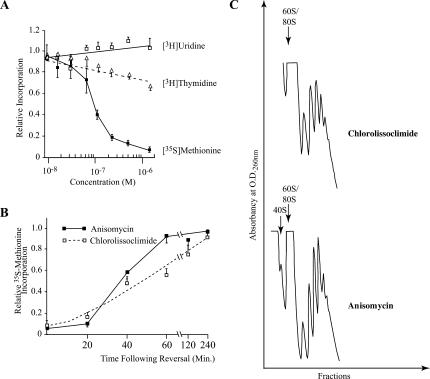
FIGURE 3.
Effect of chlorolissoclimide on protein, DNA and RNA synthesis in vivo. (A) The rate of macromolecular synthesis (TCA precipitable cpm for the indicated labeling period) obtained in the presence of increasing amounts of chlorolissoclimide was normalized to the rate obtained in the presence of vehicle (0.5% methanol) and is plotted. The results are shown for three experiments, and the SEM is presented. The rate of 35S-methionine incorporation obtained with the control reaction was 21,782 cpm/μg of protein/15-min incubation. The rate of 3H-thymidine and 3H-uridine incorporation obtained with the control reaction was 4920 cpm/μg of protein/15 min and 5560 cpm/μg of protein/20 min, respectively. (B) Inhibition of protein synthesis by chlorolissoclimide is reversible in vivo. HeLa cells were incubated for 1 h with 6.25 μM chlorolissoclimide after which time cells were washed and fresh medium added. Fifteen minutes before harvesting, cells were incubated with 35S-methionine and incorporation into protein determined by TCA precipitation. The rate of 35S-methionine incorporation obtained in the control reaction was 39,725 cpm/μg of protein/15-min incubation. Results are expressed relative to the incorporation in the presence of 0.5% methanol and represent the average of two experiments (each performed in duplicate). (C) Chlorolissoclimide does not disrupt cellular polysomes. HeLa cells were incubated for 1 h with 50 uM of chlorolissoclimide, after which the cells were washed twice with PBS, harvested with a rubber policeman, and collected by brief centrifugation. The cell pellet was resuspended in lysis buffer (5 mM Tris-HCl at pH 7.5, 2.5 mM MgCl2, 1.5 mM KCl, 0.5% Triton X-100, 0.5% sodium deoxycholate, 2 mM DTT), vortexed, and centrifuged for 2 min at 14,000g. The supernatants were loaded onto 10%–50% sucrose gradients prepared in 20 mM Hepes (pH 7.6), 100 mM KCl, and 5 mM MgCl2 and centrifuged in an SW40 at 35,000 rpm for 2 h. Gradients were analyzed by piercing the tube with a Brandel tube piercer, passing 60% sucrose through the bottom of the tube, and monitoring the absorbance of the material eluting from the tube using an ISCO UA-6 UV detector.