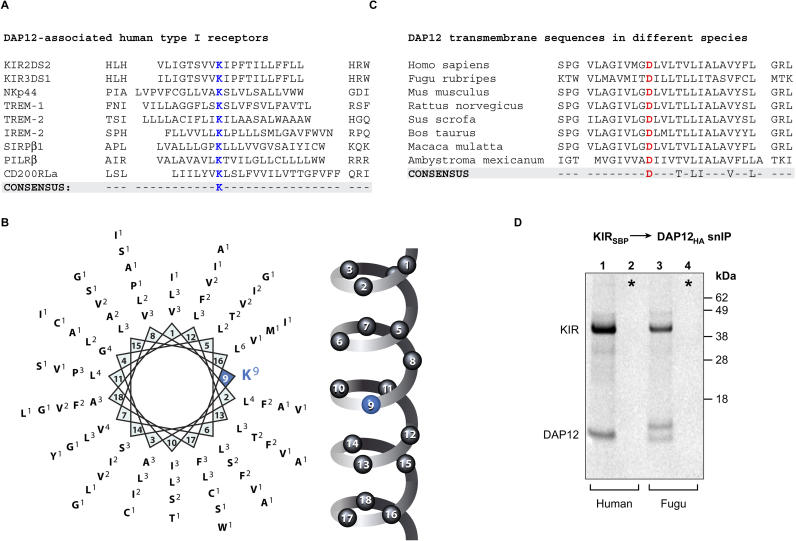
Figure 1. Structural Diversity of TM Domains among Receptors That Assemble with the DAP12 Signaling Dimer.
(A) Alignment of TM domains and flanking sequences from DAP12-associated human receptors centered on the basic TM residue that is important for receptor assembly with DAP12.
(B) Helical wheel representation of the TM residues of DAP12-associated receptors. The frequency of a given amino acid at a particular position is indicated in superscript.
(C) Alignment of the DAP12 TM domains and flanking sequences of diverse species from mammals to fish.
(D) Assembly of the human KIR receptor with human and puffer fish (F. rubripes) DAP12. In vitro assembly reactions were performed as described in Materials and Methods, and were analyzed by snIP targeting SBP-tagged KIR and HA-tagged DAP12. Radiolabeled proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, transferred to polyvinylidene fluoride membranes, and exposed to a phosphor imager plate. In control reactions (denoted by asterisks), KIR and DAP12 proteins were translated separately and combined prior to membrane solubilization. The image shown is representative of three experiments.