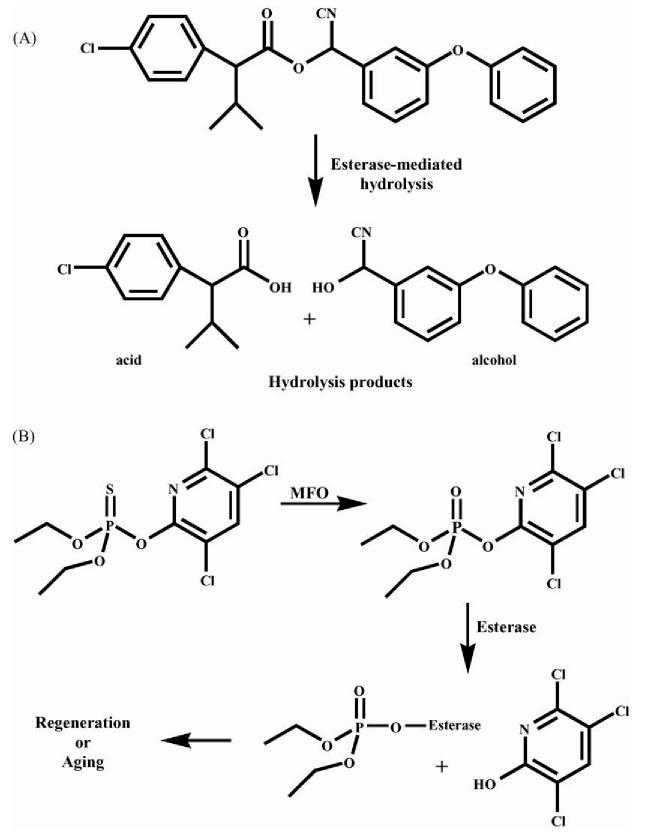
Fig. 1.
Esterase detoxification mechanisms. (A) The pyrethroid esfenvalerate is hydrolyzed by esterase to the corresponding acid and alcohol. This process reduces the toxicity of the pyrethroid. (B) The organophosphate chlorpyrifos is converted by mixed-function oxidases (MFO) to the active oxon form, which in turn inhibits esterase. After inhibition, the enzyme can go through two different pathways; regeneration, where the enzyme regains catalytic activity, or aging, in which catalytic activity is lost.