Abstract
Passive transfer of immunity to Taenia taeniaeformis infection in the rat was achieved with serum taken 14, 21 and 28 days after infection, with maximal activity at 28 days. The protective capacity resided in the globulin fraction, which was further fractionated by gel filtration and anion exchange chromatography. The immunoglobulins present in each passively transferred fraction were detected with specific antisera to 7Sγ2, 7Sγ1, γM and γA. Protective activity was confined to those fractions containing 7S immunoglobulin. Fractions enriched for γM were unable to confer protection and it was possible to protect recipient rats against challenge with fractions devoid of γA and reaginic antibody activity. 7Sγ2a antibodies were able to confer passive protection when given alone, and probably contributed to the protective capacity of mixtures containing 7Sγ2 and 7Sγ1 immunoglobulins. A mechanism for specific acquired resistance to T. taeniaeformis is proposed based upon the recently established biological properties of 7Sγ2a.
Absorption of protective activity from immune rat serum was unsuccessful using a variety of techniques, and an explanation is offered for this finding.
The results are discussed in relation to the current understanding of acquired resistance in cysticercosis and hydatid disease in domesticated food animals.
Full text
PDF





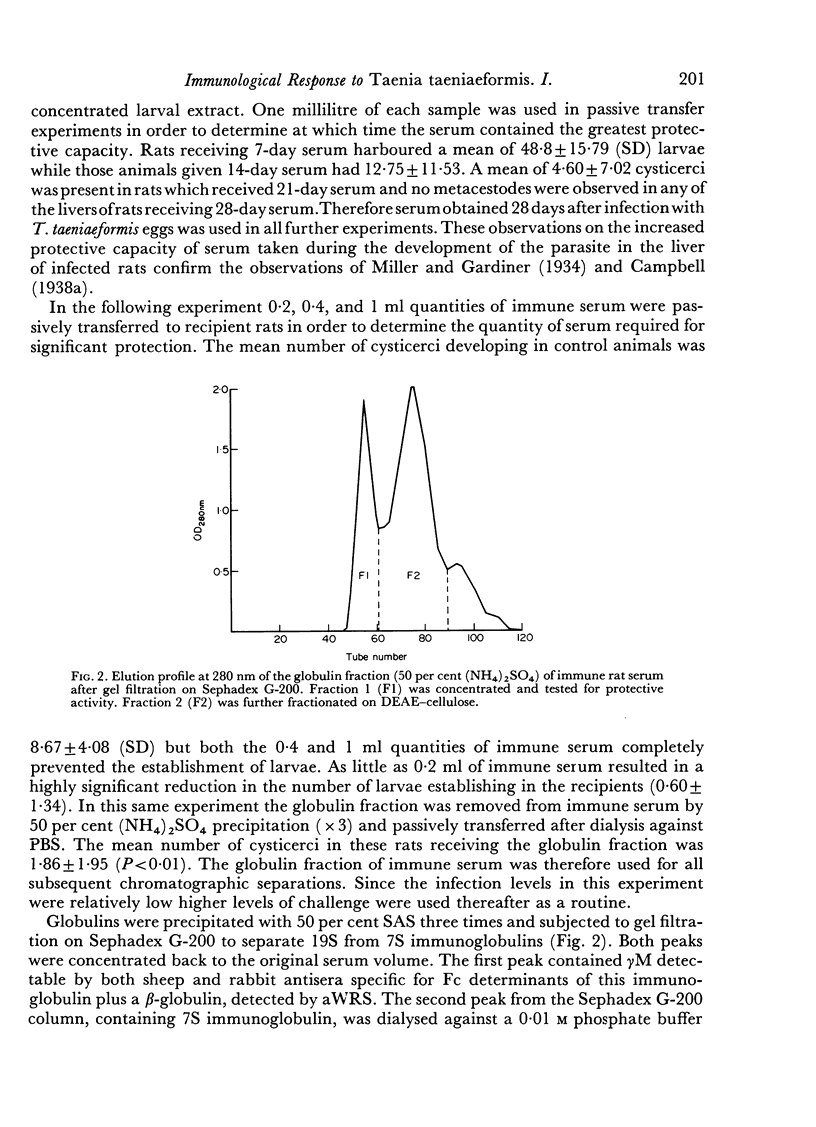
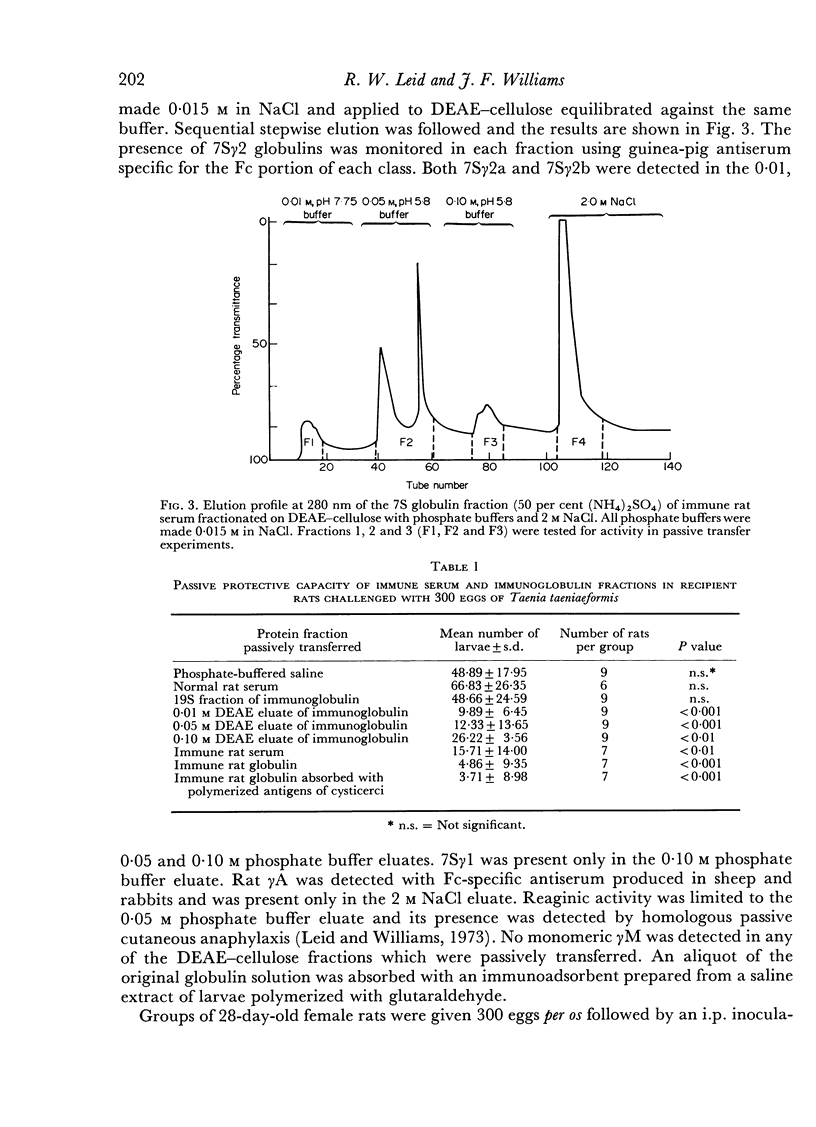
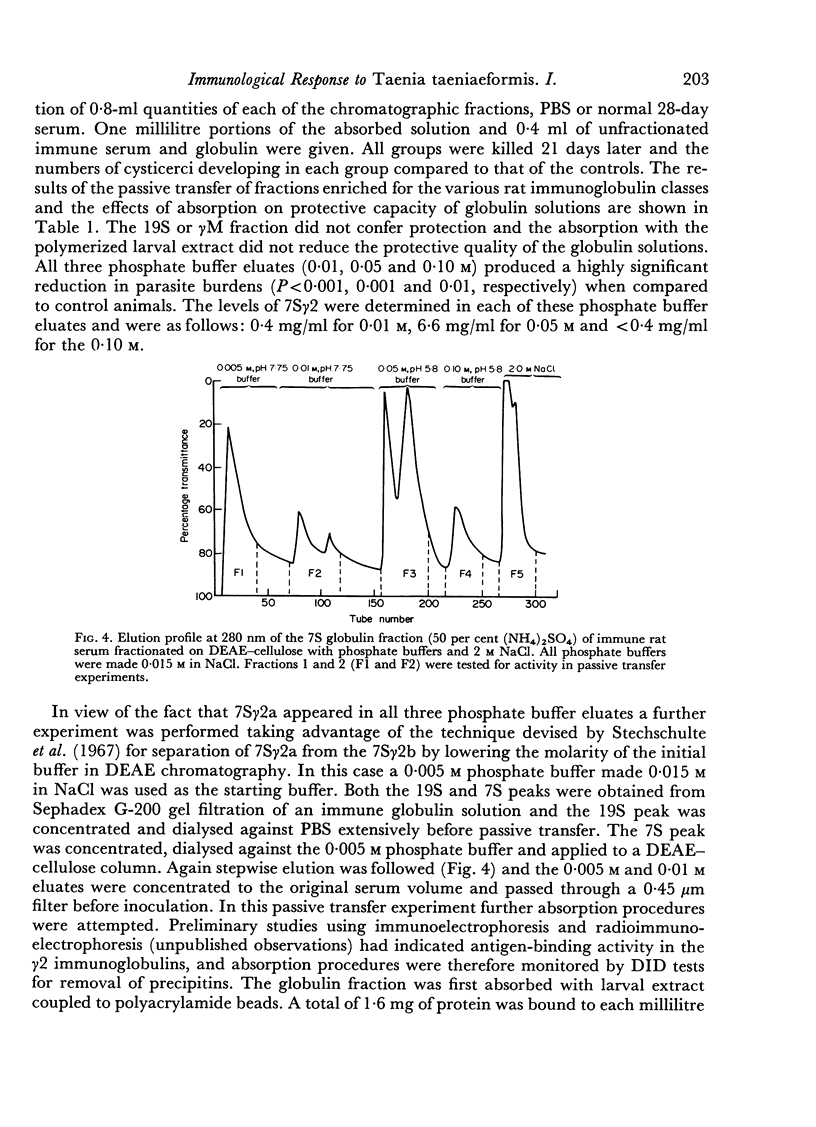
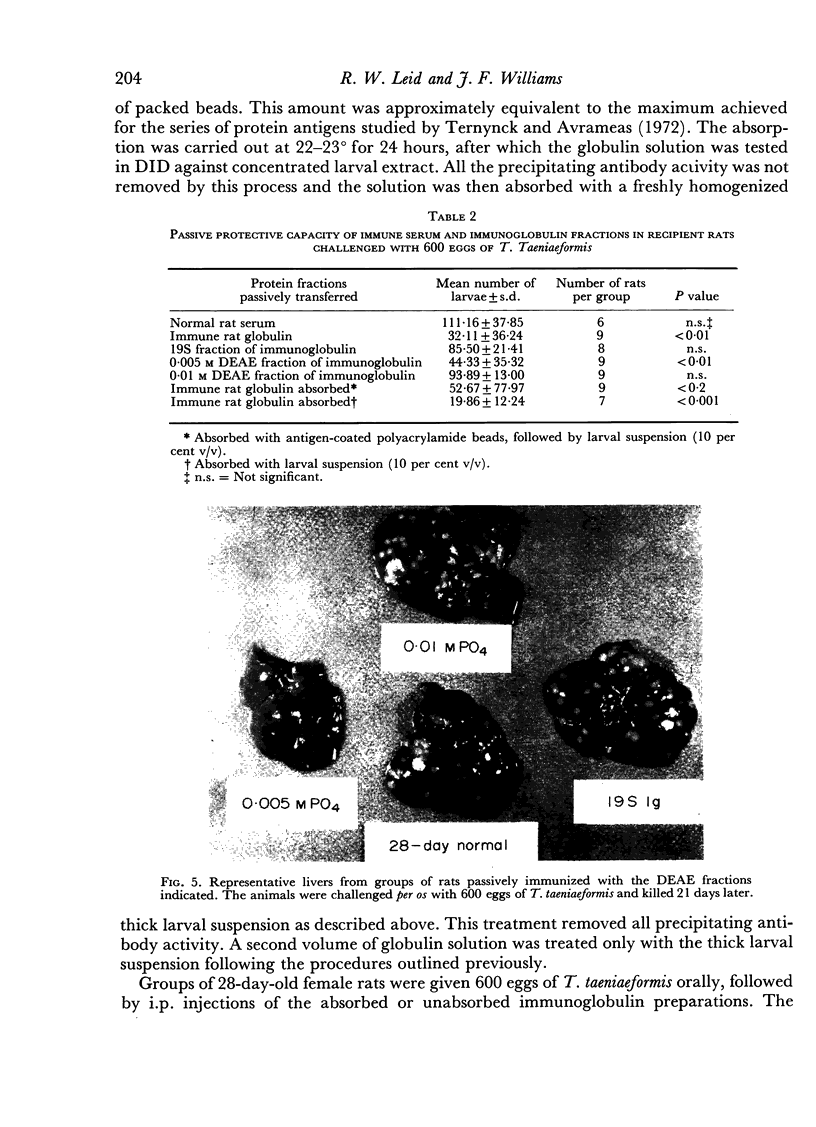




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avrameas S., Ternynck T. The cross-linking of proteins with glutaraldehyde and its use for the preparation of immunoadsorbents. Immunochemistry. 1969 Jan;6(1):53–66. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(69)90178-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binaghi R., Oriol R. Anticorps purifiés de type macroglobuline. Bull Soc Chim Biol (Paris) 1968 Sep 28;50(5):1035–1040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloch K. J., Morse H. C., 3rd, Austen K. F. Biologic properties of rat antibodies. I. Antigen-binding by four classes of anti-DNP antibodies. J Immunol. 1968 Oct;101(4):650–657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blundell S. K., Gemmell M. A., Macnamara F. N. Immunological responses of the mammalian host against tapeworm infections. VI. Demonstration of humoral immunity in sheep induced by the activated embryos of Taenia hydatigena and T. ovis. Exp Parasitol. 1968 Aug;23(1):79–82. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(68)90044-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemmell M. A., Blundell-Hasell S. K., Macnamara F. N. Immunological responses of the mammalian host against tapeworm infections. IX. The transfer via colostrum of immunity to Taenia hydatigena. Exp Parasitol. 1969 Sep;26(1):52–57. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(69)90094-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemmell M. A. Hydatidosis and cysticercosis. I. Acquired resistance to the larval phase. Aust Vet J. 1969 Nov;45(11):521–524. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1969.tb07882.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henney C. S., Ishizaka K. A simplified procedure for the preparation of immunoglobulin-class-specific antisera. J Immunol. 1969 Jul;103(1):56–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones V. E., Edwards A. J., Ogilvie B. M. The circulating immunoglobulins involved in protective immunity to the intestinal stage of Nippostrongylus brasiliensis in the rat. Immunology. 1970 May;18(5):621–633. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones V. E. Rat 7S immunoglobulins: characterization of gamma-2- and gamma-1-anti-haptens antibodies. Immunology. 1969 May;16(5):589–599. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leid R. W., Williams J. F. The immunological response of the rat to infection with Taenia taeniaeformis. II. Characterization of reaginic antibody and an allergen associated with the larval stage. Immunology. 1974 Aug;27(2):209–225. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse H. C., 3rd, Bloch K. J., Austen K. F. Biologic properties of rat antibodies. II. Time-course of appearance of antibodies involved in antigen-induced release of slow reacting substance of anaphylaxis (SRS-A rat); association of this activity with rat IgGa. J Immunol. 1968 Oct;101(4):658–663. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murrell K. D. The effect of antibody on the permeability control of larval Taenia taeniaeformis. J Parasitol. 1971 Aug;57(4):875–880. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash D. R., Vaerman J. P., Bazin H., Heremans J. F. Identification of IgA in rat serum and secretions. J Immunol. 1969 Jul;103(1):145–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogilvie B. M. Immunoglobulin responses in parasitic infections. J Parasitol. 1970 Aug;56(4):525–534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oriol R., Binaghi R., Boussac-Aron Y. Préparation d'anticorps monospécifiques anti-immunoglobulines. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1968 Jun;114(6):713–726. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rickard M. D., Bell K. J. Immunity produced against Taenia ovis and T. taeniaeformis infection in lambs and rats following in vivo growth of their larvae in filtration membrane diffusion chambers. J Parasitol. 1971 Jun;57(3):571–575. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHEIDEGGER J. J. Une micro-méthode de l'immuno-electrophorèse. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1955;7(2):103–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs D. H., Painter E. Improved flow rates with porous sephadex gels. Science. 1972 Feb 18;175(4023):781–782. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4023.781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saif L. J., Bohl E. H., Gupta R. K. Isolation of porcine immunoglobulins and determination of the immunoglobulin classes of transmissible gastroenteritis viral antibodies. Infect Immun. 1972 Oct;6(4):600–609. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.4.600-609.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stechschulte D. J., Austen K. F., Bloch K. J. Antibodies involved in antigen-induced release of slow reacting substance of anaphylaxis (SRS-A) in the guinea pig and rat. J Exp Med. 1967 Jan 1;125(1):127–147. doi: 10.1084/jem.125.1.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stechschulte D. J., Austen K. F. Immunoglobulins of rat colostrum. J Immunol. 1970 May;104(5):1052–1062. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweatman G. K. Acquired Immunity In Lambs Infected With Taenia Hydatigena Pallas, 1766. Can J Comp Med Vet Sci. 1957 Mar;21(3):65–71. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ternynck T., Avrameas S. Polyacrylamide-protein immunoadsorbents prepared with glutaraldehyde. FEBS Lett. 1972 Jun 1;23(1):24–28. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80274-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- URQUHART G. M. Epizootiological and experimental studies on bovine cysticercosis in East Africa. J Parasitol. 1961 Dec;47:857–869. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vriesman P. J., Feldman J. D. Rat M immunoglobulin: isolation and some biological characteristics. Immunochemistry. 1972 May;9(5):525–534. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(72)90062-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R. J. Gamma 1-antibodies in guinea-pigs infected with the cattle lungworm. Immunology. 1966 Sep;11(3):199–209. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





