Abstract
Secretory IgA antibodies to Vibrio cholerae were purified from the parotid saliva and mammary secretions of locally and orally immunized dogs using gel filtration, ion-exchange chromatography and anti-immunoglobulin immuno-absorbents. IgM and IgG antibodies were isolated from serum by gel filtration and ion-exchange chromatography. IgA antibodies proved to have minimal, if any, activity in direct killing of bacteria in the presence of complement or in the promotion of phagocytosis. The minimal activity which IgA had in these assays could be accounted for by extremely small quantities of IgM antibody. The same IgA antibodies, mixed with the challenge innoculum of Vibrio cholerae and fed to infant mice, protected these mice as efficiently as IgG or IgM antibodies.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adinolfi M., Glynn A. A., Lindsay M., Milne C. M. Serological properties of gamma-A antibodies to Escherichia coli present in human colostrum. Immunology. 1966 Jun;10(6):517–526. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adinolfi M., Mollison P. L., Polley M. J., Rose J. M. Gamma-A-blood group antibodies. J Exp Med. 1966 May 1;123(5):951–967. doi: 10.1084/jem.123.5.951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auzins I. A comparative assay of O-somatic antigen 5 of Salmonellae. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1968 Feb;46(1):93–105. doi: 10.1038/icb.1968.8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOMBS R. R. A., GLEESON-WHITE M. H., HALL J. G. Factors influencing the agglutinability of red cells. II. The agglutination of bovine red cells previously classified as "inagglutinable" by the building up of an "anti-globulin: globulin lattice" on the sensitized cells. Br J Exp Pathol. 1951 Jun;32(3):195–202. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eddie D. S., Schulkind M. L., Robbins J. B. The isolation and biologic activities of purified secretory IgA and IgG anti-Salmonella typhimurium "O" antibodies from rabbit intestinal fluid and colostrum. J Immunol. 1971 Jan;106(1):181–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fubara E. S., Freter R. Protection against enteric bacterial infection by secretory IgA antibodies. J Immunol. 1973 Aug;111(2):395–403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heddle R. J., Knop J., Steele E. J., Rowley D. The effect of lysozyme on the complement-dependent bactericidal action of different antibody classes. Immunology. 1975 Jun;28(6):1061–1066. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
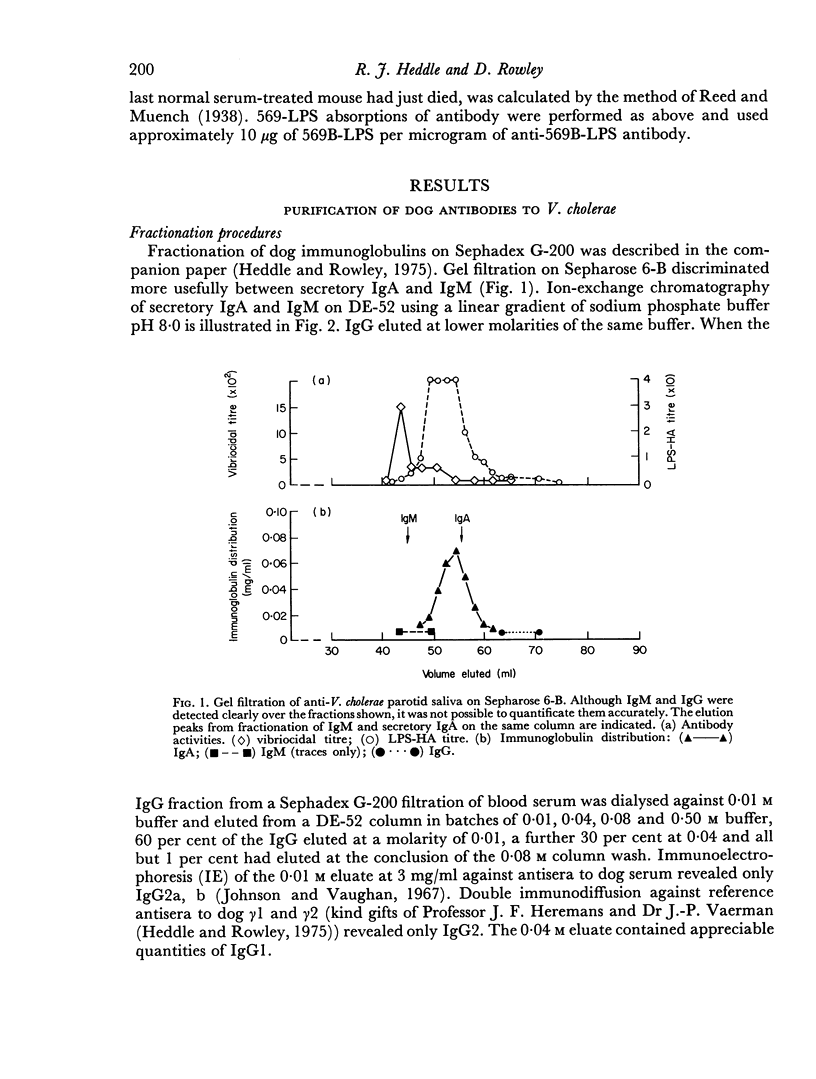
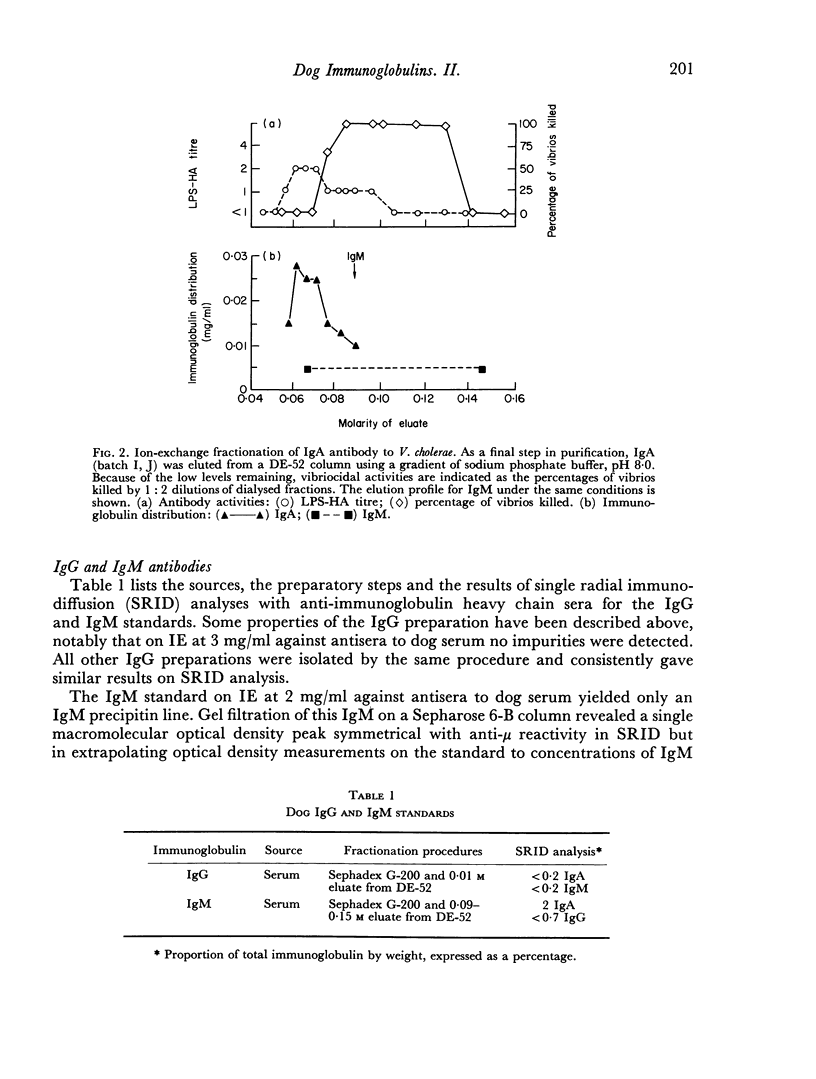
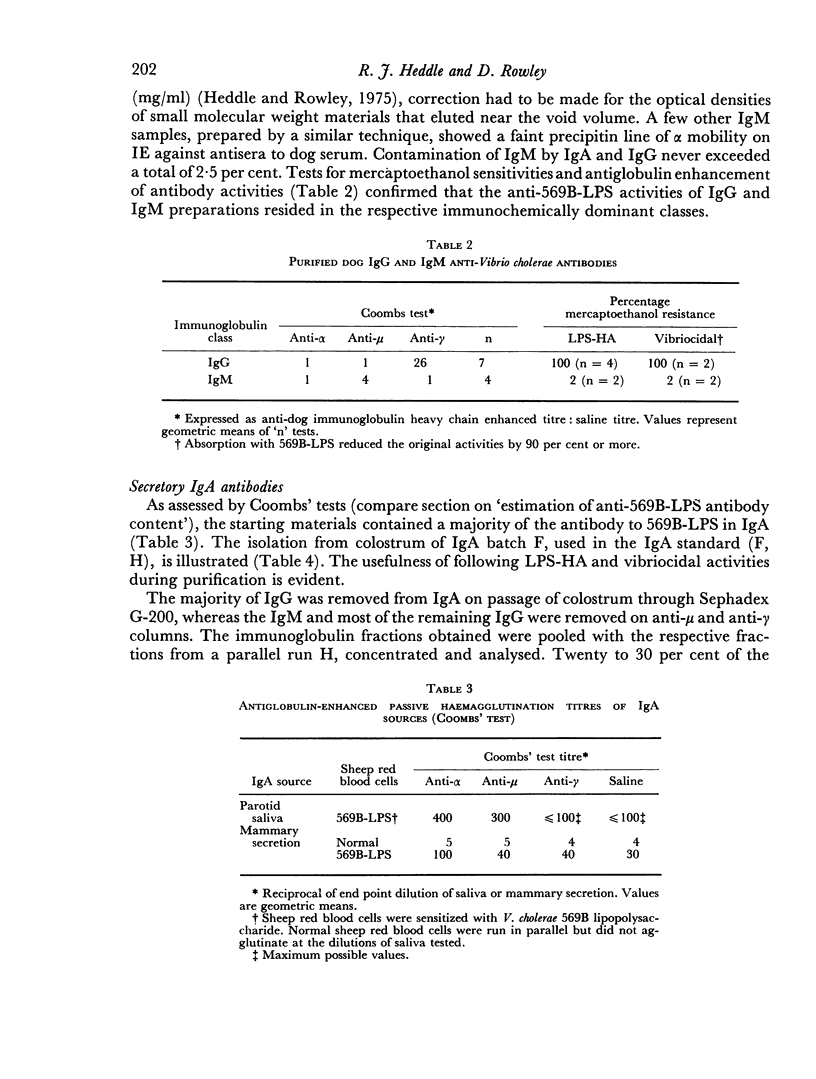
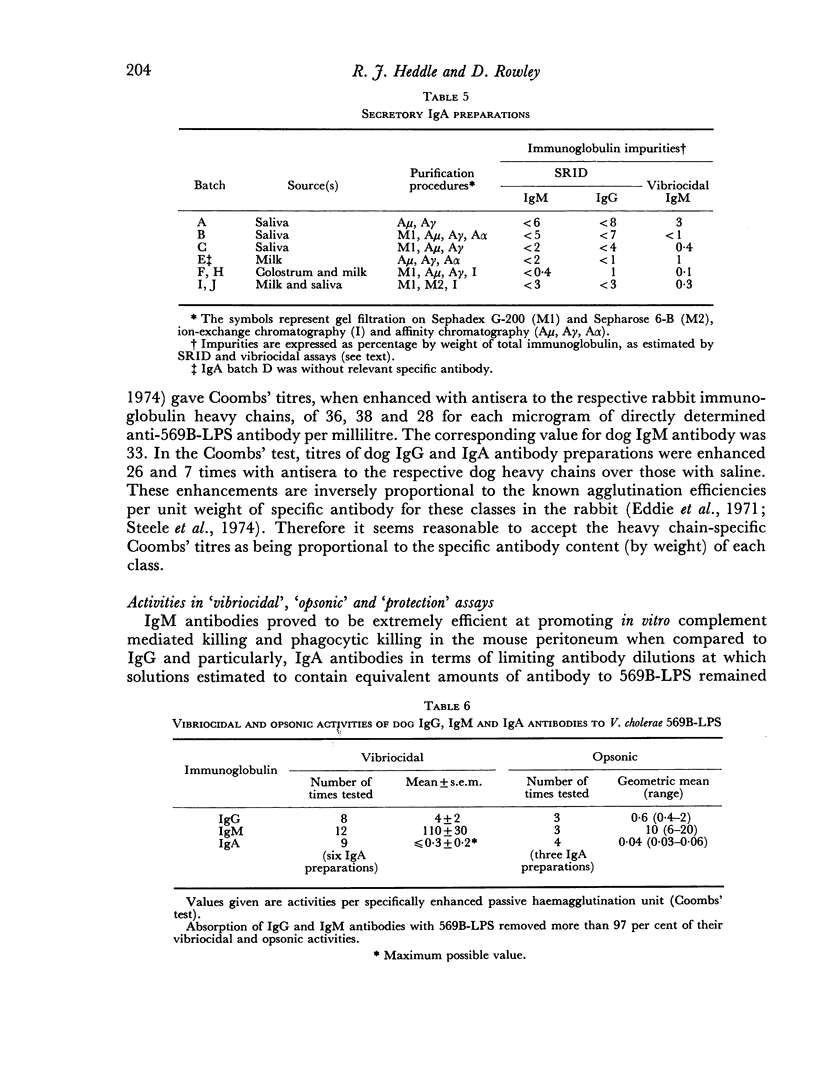
- Heddle R. J., Rowley D. Dog immunoglobulins. I. immunochemical characterization of dog serum, parotid saliva, colostrum, milk and small bowel fluid. Immunology. 1975 Jul;29(1):185–195. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill I. R., Porter P. Studies of bactericidal activity to Escherichia coli of porcine serum and colostral immunoglobulins and the role of lysozyme with secretory IgA. Immunology. 1974 Jun;26(6):1239–1250. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka T., Ishizaka K., Borsos T., Rapp H. C'-1 fixation by human isoagglutinins: fixation of C'-1 by gamma-G and gamma-M but not by gamma-A antibody. J Immunol. 1966 Nov;97(5):716–726. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENKIN C. R., ROWLEY D. The importance of antibody in the prevention of experimental cholera in rabbits. Br J Exp Pathol. 1960 Feb;41:24–30. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. S., Vaughan J. H. Canine immunoglobulins. I. Evidence for six immunoglobulin classes. J Immunol. 1967 May;98(5):923–934. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan M. E., Dalmasso A. P., Woodson M. Complement-dependent opsonization of incompatible erythrocytes by human secretory IgA. J Immunol. 1972 Jan;108(1):275–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knop J., Breu H., Wernet P., Rowley D. The relative antibacterial efficiency of IgM, IgG and IgA from pig colostrum. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1971 Aug;49(4):405–413. doi: 10.1038/icb.1971.42. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neoh S. H., Rowley D. The antigens of Vibrio cholerae involved in the vibriocidal action of antibody and complement. J Infect Dis. 1970 May;121(5):505–513. doi: 10.1093/infdis/121.5.505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pike R. M. Antibody heterogeneity and serological reactions. Bacteriol Rev. 1967 Jun;31(2):157–174. doi: 10.1128/br.31.2.157-174.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quie P. G., Messner R. P., Williams R. C., Jr Phagocytosis in subacute bacterial endocarditis. Localization of the primary opsonic site to Fc fragment. J Exp Med. 1968 Oct 1;128(4):553–570. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.4.553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBBINS J. B., KENNY K., SUTER E. THE ISOLATION AND BIOLOGICAL ACTIVITIES OF RABBIT GAMMA M- AND GAMMA G-ANTI-SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM ANTIBODIES. J Exp Med. 1965 Aug 1;122:385–402. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.2.385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steele E. J., Chaicumpa W., Rowley D. Isolation and biological properties of three classes of rabbit antibody to Vibrio cholerae. J Infect Dis. 1974 Aug;130(2):93–103. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.2.93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITBY J. L., ROWLEY D. The role of macrophages in the elimination of bacteria from the mouse peritoneum. Br J Exp Pathol. 1959 Aug;40:358–370. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson I. D. Studies on the opsonic activity of human secretory IgA using an in vitro phagocytosis system. J Immunol. 1972 Mar;108(3):726–730. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zipursky A., Brown E. J., Bienenstock J. Lack of opsonization potential of 11S human secretory A. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1973 Jan;142(1):181–184. doi: 10.3181/00379727-142-36983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


