Abstract
Normal murine peritoneal macrophages were rendered cytotoxic against 51Cr-labelled allogeneic and syngeneic target cells by incubation with supernatant of selected cell cultures.'Active' culture supernatant was produced both by specifically sensitized cytotoxic T lymphocytes as well as by mitogen-stimulated T cells, but not by mitogen-stimulated B cells. The in vitro induced macrophage-mediated cytotoxicity was found to be non-specific in the sense that 51Cr-labelled target cells of different H-2 haplotype were lysed equally well.
Full text
PDF


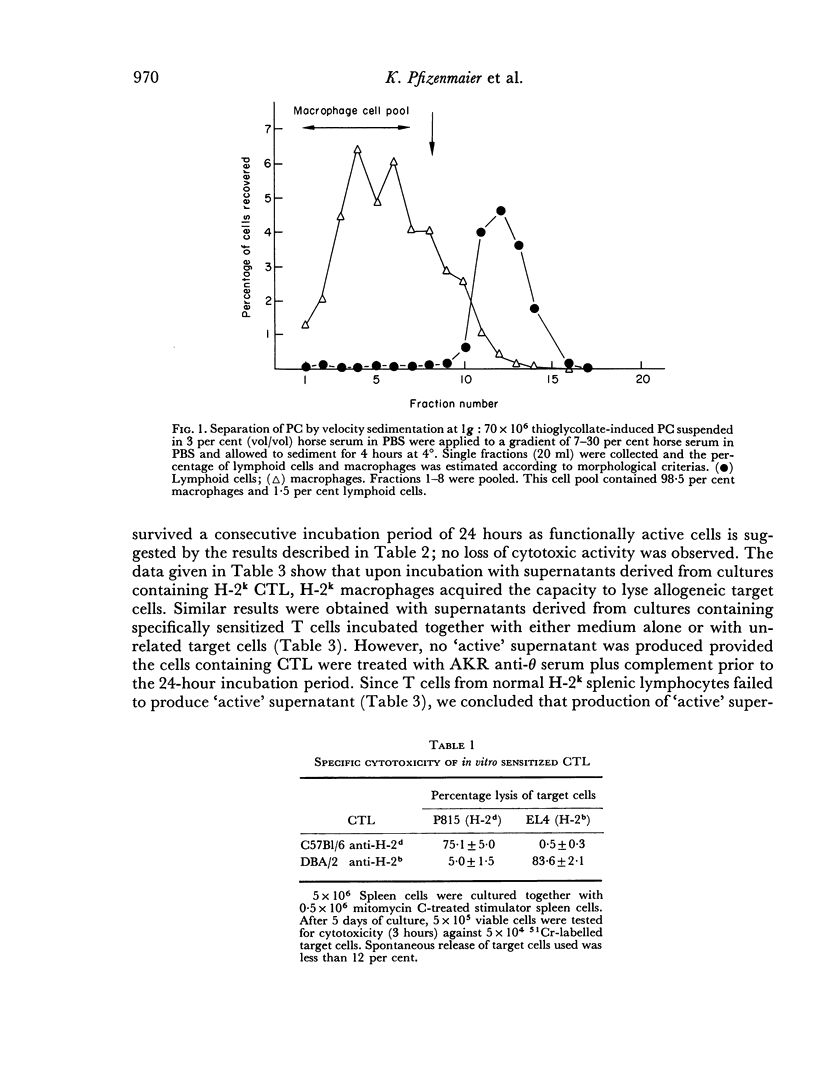
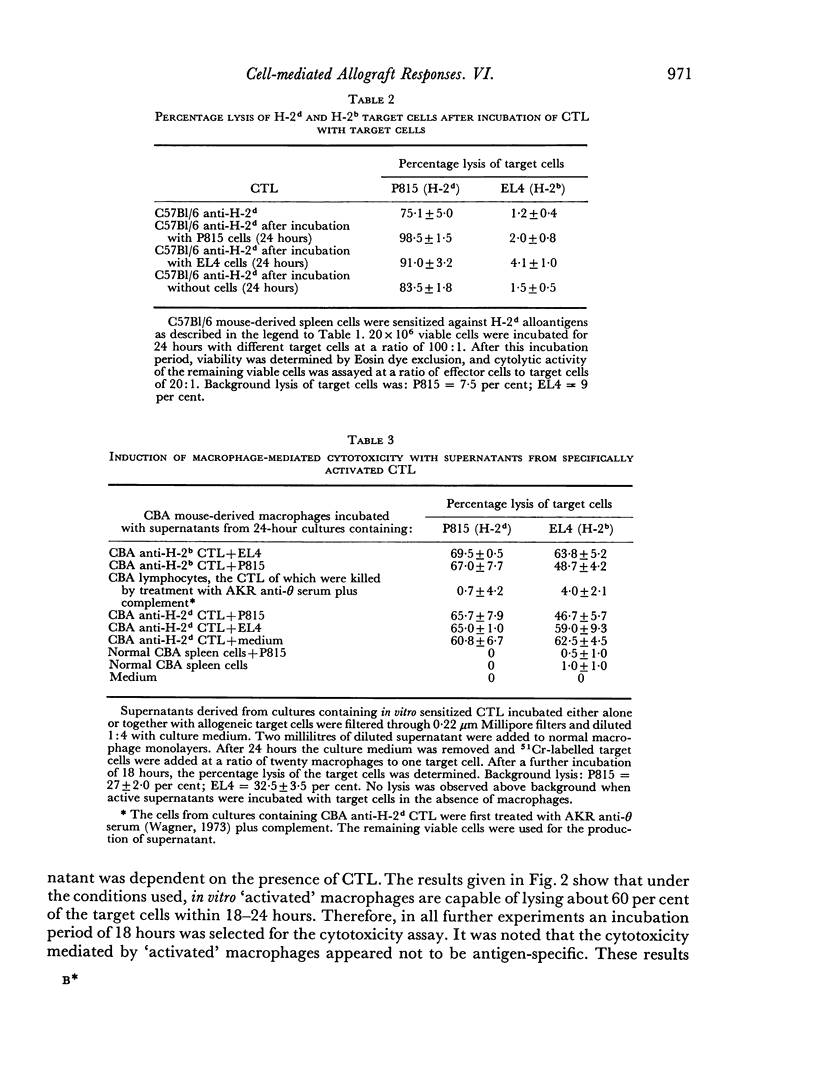
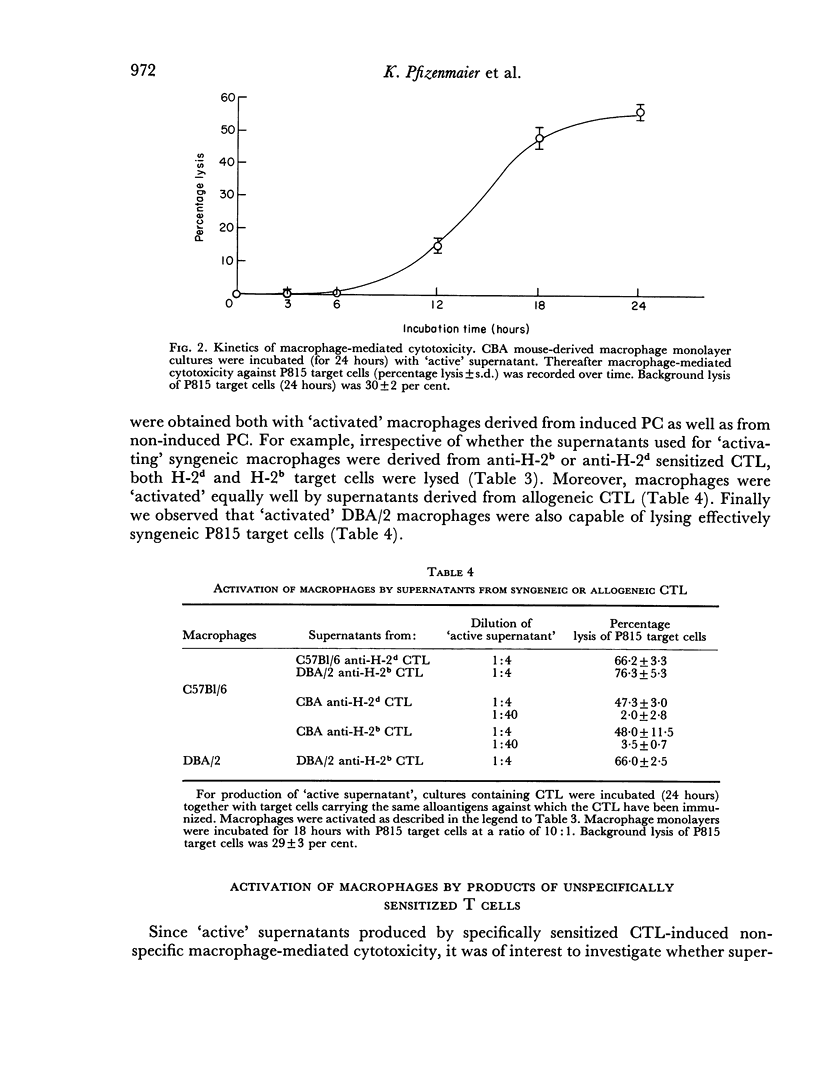
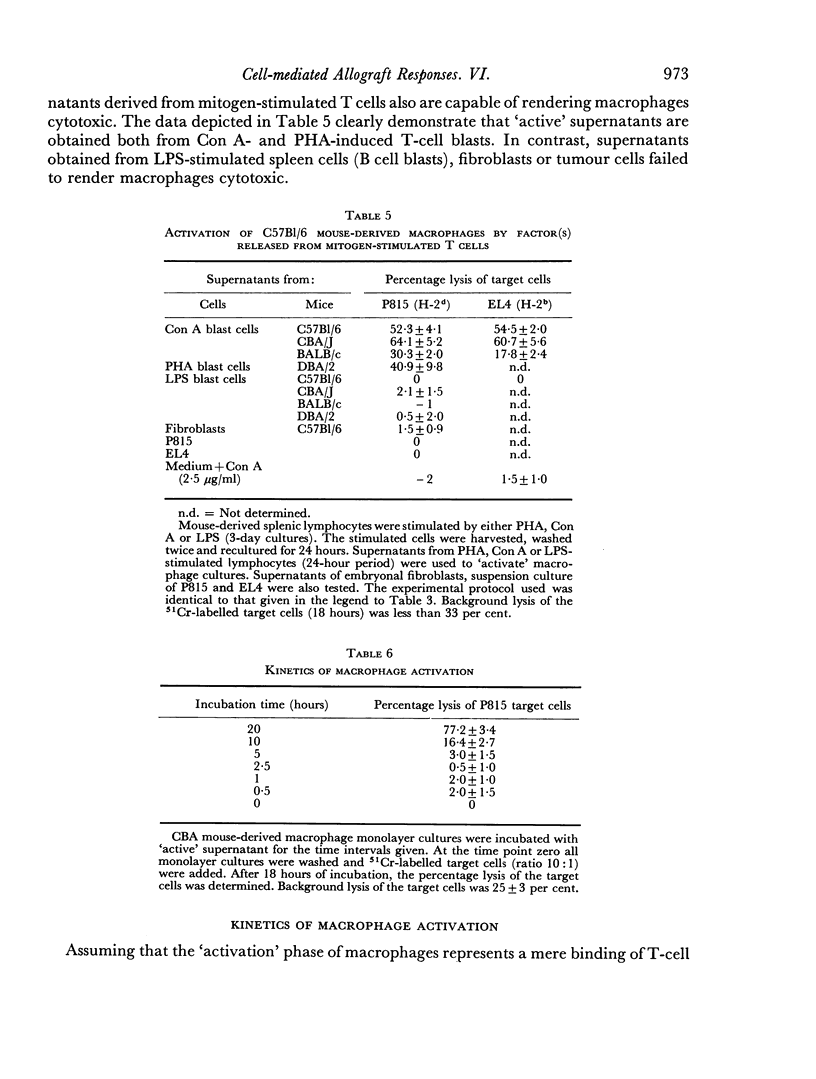



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berke G., Amos D. B. Mechanism of lymphocyte-mediated cytolysis. The LMC cycle and its role in transplantation immunity. Transplant Rev. 1973;17(0):71–107. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1973.tb00124.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerottini J. C., Brunner K. T. Cell-mediated cytotoxicity, allograft rejection, and tumor immunity. Adv Immunol. 1974;18:67–132. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60308-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Den Otter W., Evans R., Alexander P. Cytotoxicity of murine peritoneal macrophages in tumour allograft immunity. Transplantation. 1972 Aug;14(2):220–226. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197208000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimitriu A., Dy M., Thomson N., Hamburger J. Macrophage cytotoxicity in the mouse immune response against a skin allograft. J Immunol. 1975 Jan;114(1 Pt 1):195–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R., Alexander P. Mechanism of immunologically specific killing of tumour cells by macrophages. Nature. 1972 Mar 24;236(5343):168–170. doi: 10.1038/236168a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R., Cox H., Alexander P. Immunologically specific activation of macrophages armed with the specific macrophage arming factor (SMAF). Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1973 May;143(1):256–259. doi: 10.3181/00379727-143-37298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giroud J. P., Spector W. G., Willoughby D. A. Bone marrow and lymph node cells in the rejection of skin allografts in mice. Immunology. 1970 Dec;19(6):857–863. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golstein P., Wigzell H., Blomgren H., Svedmyr E. A. Cells mediating specific in vitro cytotoxicity. II. Probable autonomy of thymus-processed lymphocytes (T cells) for the killing of allogeneic target cells. J Exp Med. 1972 Apr 1;135(4):890–906. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.4.890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granger G. A., Weiser R. S. Homograft target cells: contact destruction in vitro by immune macrophages. Science. 1966 Jan 7;151(3706):97–99. doi: 10.1126/science.151.3706.97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häyry P., Andersson L. C., Nordling S., Virolainen M. Allograft response in vitro. Transplant Rev. 1972;12:91–140. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1972.tb00054.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller R. Cytostatic elimination of syngeneic rat tumor cells in vitro by nonspecifically activated macrophages. J Exp Med. 1973 Sep 1;138(3):625–644. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.3.625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohmann-Matthes M. L., Fischer H. T-cell cytotoxicity and amplification of the cytotoxic reaction by macrophages. Transplant Rev. 1973;17(0):150–171. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1973.tb00126.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohmann-Matthes M. L., Schipper H., Fischer H. Macrophage-mediated cytotoxicity against allogeneic target cells in vitro. Eur J Immunol. 1972 Feb;2(1):45–49. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830020110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohmann-Matthes M. L., Ziegler F. G., Fischer H. Macrophage cytotoxicity factor. A product of in vitro sensitized thymus-dependent cells. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Jan;3(1):56–58. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830030112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLennan I. C., Loewi G., Howard A. A human serum immunoglobulin with specificity for certain homologous target cells, which induces target cell damage by normal human lymphocytes. Immunology. 1969 Dec;17(6):897–910. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melsom H., Seljelid R. The cytotoxic effect of mouse macrophages on syngeneic and allogeneic erythrocytes. J Exp Med. 1973 Mar 1;137(3):807–820. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.3.807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. G., Phillips R. A. Separation of cells by velocity sedimentation. J Cell Physiol. 1969 Jun;73(3):191–201. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040730305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmann P., Holm G. Cytotoxic effects of lymphoid cells in vitro. Adv Immunol. 1969;11:117–193. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60479-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schirrmacher V., Rubin B., Pross H., Wigzell H. Cytotoxic immune cells with specificity for defined soluble antigens. IV. Antibody as mediator of specific cytotoxicity. J Exp Med. 1974 Jan 1;139(1):93–107. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.1.93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinitz M., Weiss D. W. Studies on the physiological manifestations of cell-mediated cytotoxicity. I. Early metabilic changes in mouse plasmacytoma cells exposed in vitro to sensitized allogeneic splenocytes. Cell Immunol. 1975 Feb;15(2):403–418. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(75)90018-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner H., Röllinghoff M. T cell-mediated cytotoxicity: discrimination between antigen recognition, lethal hit and cytolysis phase. Eur J Immunol. 1974 Nov;4(11):745–750. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830041108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner H. Synergy during in vitro cytotoxic allograft responses. I. Evidence for cell interaction between thymocytes and peripheral T cells. J Exp Med. 1973 Dec 1;138(6):1379–1397. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.6.1379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zbar B., Wepsic H. T., Borsos T., Rapp H. J. Tumor-graft rejection in syngeneic guinea pigs: evidence for a two-step mechanism. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1970 Feb;44(2):473–481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler F. G., Lohmann-Matthes M. L., Fischer H. Studies on the mechanism of macrophage-mediated cytotoxicity. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1975;48(2):182–191. doi: 10.1159/000231304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


