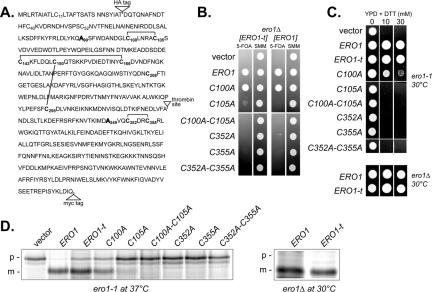
Figure 1.
Functionality of Ero1p-t. (A) Ero1p amino acid sequence depicting insertion of two epitope tags (HA and myc), replacement of Cys90 and Cys349 with Ala, and addition of a thrombin protease recognition site. Lines denote cysteine connectivity found in the Ero1p-c crystal structure. (B) Complementation of an ero1Δ mutant by ERO1-t alleles. Transformants of CKY933 (ero1Δ [pAF82]) containing the following plasmids were selected on SMM minus leucine and spotted onto SMM plates containing 5-FOA or SMM plates lacking leucine: pCS253, pCS257, pCS258, pCS259, pCS254, pCS255, pCS256, pAF89, pAF125, pAF126, pCS214, pAF129, pAF130, pCS261, or an empty vector. (C) Transformants of CKY598 (ero1-1) or ero1Δ cells containing the ERO1-t plasmids in B were grown overnight in SMM minus leucine and spotted onto YPD plates containing the indicated amounts of DTT. Strains were grown for 2 d at 30°C. (D) Processing of newly synthesized CPY in CKY598 (ero1-1) or ero1Δ cells containing the ERO1-t plasmids in B. Cells were radiolabeled at 30 or 38°C for 30 min, and CPY was immunoprecipitated and resolved by SDS-PAGE. ER (p1) and vacuolar mature (m) forms of CPY are indicated.