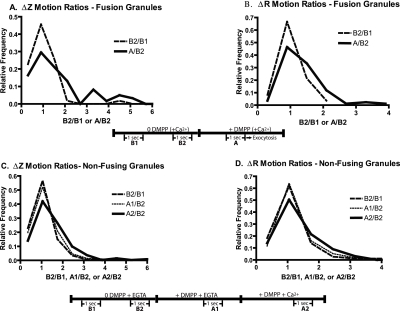
Figure 5.
Nicotininc stimulation causes Ca2+-dependent increases in granule motion. Chromaffin cells were transiently transfected with a plasmid encoding VAMP-GFP, which labels secretory granules. (A and B) Cells were visualized with TIRFM for 5 s before stimulation with the nicotinic agonist DMPP in the presence of 2.2 mM Ca2+. The noise-corrected z and R motions of individual granules that underwent secretion were determined during two 1-s intervals (10 Hz, frame acquisition) before stimulation (B1 and B2) and then during a 1-s interval 1.2-0.2 s before exocytosis. Ratios of the mean motions immediately before exocytosis to that before stimulation (A/B2) were calculated for each granule. Changes in motion unrelated to stimulation, B2/B1 ratios, were also determined. Motions of 59 granules in z and 84 granules in R from 19 cells were calculated. The numbers were limited to granules that could be tracked from the beginning of the experiment with motions at least twice the estimated noise. The distributions of the ratio of motions are significantly different for A/B2 versus B1/B2 for Δz and ΔR (p < 0.003 and 0.0001, respectively, Mann-Whitney U test). (C and D) Effects of nicotinic stimulation on granules not undergoing exocytosis were investigated. Cells were bathed in Ca2+-free PSS with 0.1 mM EGTA and sequentially perfused with Ca2+-free PSS with 2 mM EGTA (including intervals B1 and B2), 20 μM DMPP without Ca2+ + 2 mM EGTA (including interval A1), and finally with 20 μM DMPP + 10 mM Ca2+ (including interval A2). Noise-corrected Δz and ΔR motions of greater than 330 individually tracked granules from 13 cells were determined. Mean motions during each of the 1-s intervals were determined and the indicated ratios were calculated. p < 0.001 for the distributions of both Δz and ΔR ratios of A2/B2 versus B2/B1 (Mann-Whitney U test).