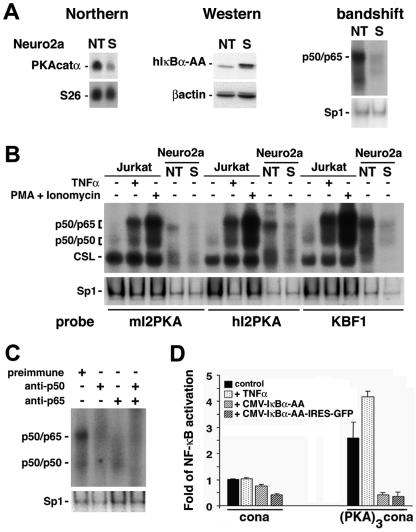
FIG. 5.
PKA catalytic α gene expression is regulated via NF-κB. (A) Northern blot analysis of total RNA (15 μg) from Neuro2a cells nontransfected (NT) or constitutively expressing the super-repressor (S). The top left blot shows hybridization with full-length mouse PKA catalytic α cDNA; in the bottom blot, the same filter was rehybridized with an S26 probe as an invariant control. Western blot (middle) analysis of protein extracts (60 μg) with a polyclonal antibody directed against IκBα (top) or a monoclonal antibody against β-actin as an internal control (bottom) confirms the overexpression of the super-repressor (human IκBα-AA [hIκBα-AA]) in the stable clone (S). Nuclear extracts (5 μg) analyzed by bandshift assay (right) for binding to a canonical κB site show high levels of nuclear p50/p65 heterodimers in nontransfected (NT) Neuro2a cells that are almost totally suppressed in the stable clone (S). The same extracts used for bandshift assays with an Sp1 site serve as an invariant control. (B) Five micrograms of nuclear extracts from Jurkat cells, untreated or treated with TNF-α (10 ng/ml) or with phorbol myristate acetate (PMA; 50 ng/ml) and ionomycin (1 μg/ml), or 0. 5 μg of nuclear extracts from nontransfected Neuro2a cells (NT) or Neuro2a cells stably expressing the super-repressor (S) were analyzed by bandshift assay for their ability to bind to κB sites identified in intron 2 of the mouse and human PKAcatα genes (mI2PKA and hI2PKA, respectively) or to a canonical κB site (KBF1). Variation in specific activities of the probes is responsible for the different intensities observed after binding with the various probes. CSL is CBF1/Su(H)L/Lag1, also known as RBP-Jk complex, which binds a half-κB site and is involved in the Notch pathway. The same extracts used for bandshift assays with an Sp1 site serve as internal controls. (C) Nuclear extracts from Neuro2a cells (5 μg) were preincubated with preimmune serum or sera directed against p50 or/and p65 and analyzed by bandshift assay for binding to the κB site from intron 2 of the mouse PKA catalytic α gene. The same extracts analyzed by bandshift assay for binding to Sp1 serve as internal controls. (D) Neuro2a cells were transfected with luciferase reporter constructs containing a minimal promoter alone (cona) or juxtaposed to a trimerized mouse intron 2 PKA κB site [(PKA)3cona] together with an EF1-lacZ normalization vector, in the absence or presence of expression vectors coding for the super-repressor (CMV-IκBα-AA or CMV-IκBα-AA-IRES-GFP, where IRES is internal ribosome entry site). Cells were left untreated or were treated with TNF-α (10 ng/ml) for 6 h and assessed for activation of the luciferase and β-galactosidase reporter genes. Data are means ± standard errors of the means.