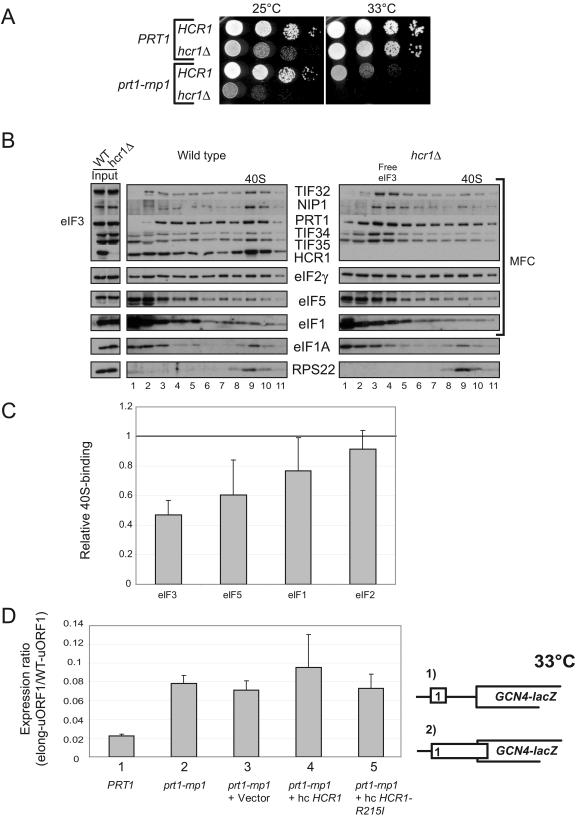
FIG. 6.
Deletion of HCR1 exacerbates the Ts− phenotype in prt1-rnp1 cells and reduces 40S binding of eIF3 in PRT1 cells. (A) Serial dilutions of PRT1 (H2879), prt1-rnp1 (H3674), hcr1Δ (H3675), and prt1-rnp1 hcr1Δ (H3676) cells were spotted on YPD and incubated at 25 or 33°C for 2 and 2.5 days, respectively. (B and C) Analysis of 40S-bound eIFs in HCHO cross-linked cells of HCR1 (H2879) and hcr1Δ (H3675) strains was conducted and quantified essentially as described in Fig. 3A and B, based on four independent experiments. (D) The prt1-rnp1 mutation leads to leaky scanning that is not suppressed by hc HCR1-R215I. PRT1 strain H2879, prt1-rnp1 strain H3674, or transformants of H3674 harboring vector YEplac181, hc-HCR1 (p3778), or hc-HCR1-R215I (p3780) were transformed with pM199 containing a GCN4-lacZ construct with uORF1 alone or pM226 containing an elongated uORF1 that overlaps GCN4-lacZ in a different reading frame (shown schematically as constructs 1 and 2, respectively). Cells were grown in SC-Ura at 33°C, and β-galactosidase activities were measured in WCEs and are expressed in units of nanomoles of o-nitrophenyl-β-d-galactopyranoside hydrolyzed per minute per milligram of protein. Τhe activity measured for pM226 was normalized to that for pM199, and the normalized values from at least three independent transformants were averaged to obtain the means and standard errors plotted in the histogram.