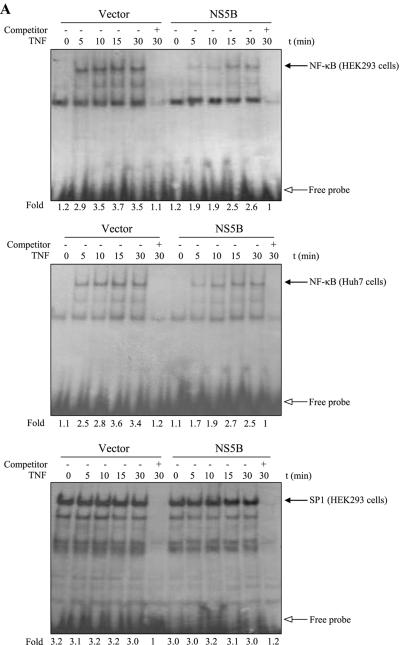
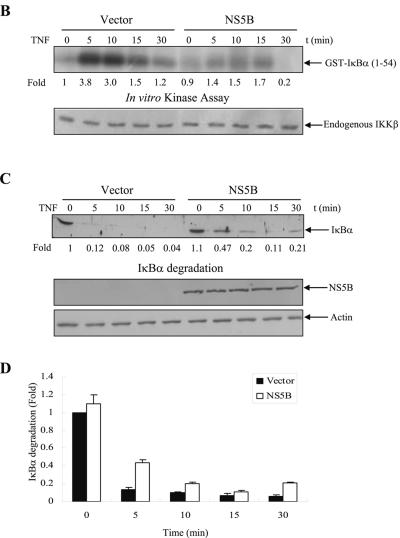
FIG.1.
The NS5B of hepatitis C virus inhibits TNF-α-induced NF-κB and IKK activations. (A) NS5B inhibits TNF-α-induced NF-κB DNA binding activity. HEK293 cells and Huh7 cells were transfected with either empty vector or NS5B expression plasmid. At 24 h after transfection, cells were treated with human TNF-α (20 ng/ml) for the indicated times. Nuclear extracts were prepared and assessed for activated NF-κB by EMSA with γ-32P-labeled double-stranded NF-κB oligonucleotide (top and middle panels) and SP1 activation with double-stranded SP1 oligonucleotide (bottom panel) as described in Materials and Methods. Arrows indicate retarded DNA-protein complexes. (B) HCV NS5B protein inhibits TNF-α-induced endogenous IKKβ activation. HEK293 cells were transiently transfected with either empty vector or NS5B expression plasmid. At 24 h after transfection, cells were incubated with human TNF-α (20 ng/ml) for the indicated times. Cell lysates were then precipitated with anti-IKKβ antibody, and endogenous IKKβ kinase activity was determined using GST-IκBα (1 to 54 aa) as a substrate (upper panel). Protein levels of endogenous IKKβ in the same cell lysates were determined by immunoblotting (lower panel). (C) NS5B protein inhibits TNF-α-stimulated IκBα degradation. HEK293 cells transfected with either vector or NS5B plasmid DNA were stimulated with human TNF-α (20 ng/ml) for the indicated times. Equal amounts of cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-IκBα antibody (top panel). The results shown are representative of three independent experiments. Protein levels of HCV NS5B (middle panel) and β-actin (bottom panel) in the same cell lysates were determined by immunoblotting. (D) Triplicate experimental data of Fig. 1C were quantified, and each bar represents the average IκBα degradation.