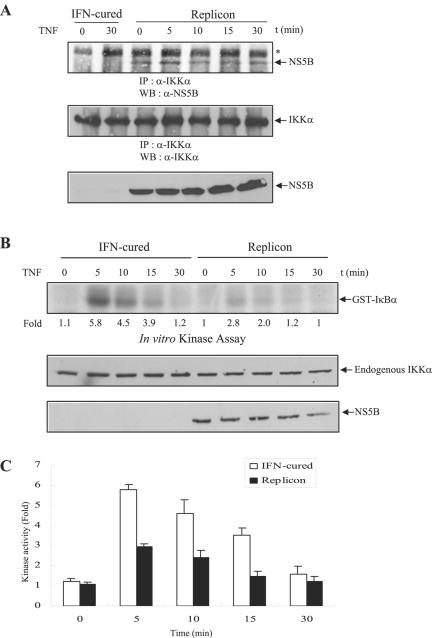
FIG. 4.
HCV subgenomic replicon cells inhibit TNF-α-induced IKKα activation through interaction with NS5B and IKKα. (A) The NS5B protein of HCV subgenomic replicon cells interacts with endogenous IKKα protein in vivo. Both IFN-cured Huh7 cells and HCV subgenomic replicon cells were treated with human TNF-α (20 ng/ml) for the indicated times. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-IKKα, and then bound proteins were immunoblotted with anti-NS5B monoclonal antibody (top panel). Membrane was reprobed with anti-IKKα polyclonal antibody to confirm the expression of endogenous IKKα (middle panel). The same cell lysates were immunoblotted with anti-NS5B monoclonal antibody to confirm the expression of NS5B protein in HCV subgenomic replicon cells (bottom panel). The asterisk indicates a nonspecific band. IP, immunoprecipitation; WB, Western blot. (B) HCV subgenomic replicon cells inhibit TNF-α-induced endogenous IKKα activation. Both IFN-cured Huh7 cells and HCV subgenomic replicon cells were incubated with human TNF-α (20 ng/ml) for the indicated times. Cell lysates were precipitated with anti-IKKα antibody, and then endogenous IKKα kinase activity was determined using GST-IκBα (1 to 54 aa) as a substrate (top panel). Protein levels of endogenous IKKα and NS5B in the same cell lysates were determined by immunoblotting with either IKKα antibody (middle panel) or NS5B antibody (bottom panel). (C) Data from triplicate experiments shown in Fig. 4B were quantified, and each bar represents the average of IKKα kinase activities.