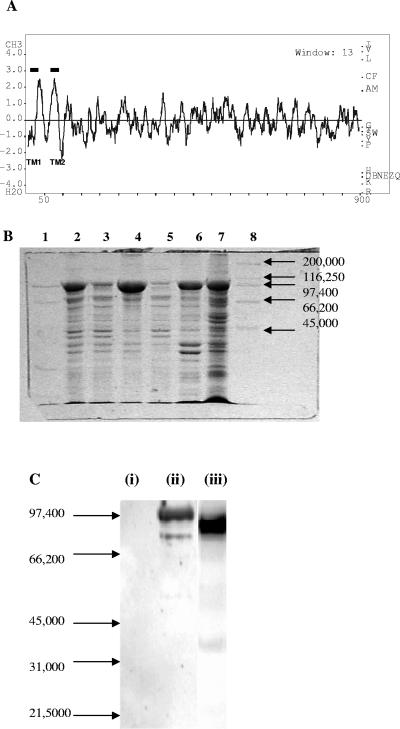
FIG. 3.
(A) Hydrophobicity profile of the CbbSR protein calculated with the BioEdit sequence alignment editor (Ibis Therapeutics, Carlsbad, CA). (B) Partial purification of the recombinant full-length CbbSR. Fractions isolated during the preparation of inner membranes from E. coli cells transformed with pQE8072 were separated on a 12% SDS-PAGE minigel. Approximately 10 μg of total protein was loaded in lanes 2 to 6; lane 7 contains 30 μg of membrane proteins. Lane 1, low-range molecular weight markers (Bio-Rad); lane 2, crude extract; lane 3, soluble fraction obtained from the 10,000 × g centrifugation; lane 4, membrane fraction obtained from the 10,000 × g centrifugation; lane 5, soluble fraction isolated at 131,000 × g; lane 6, membrane fraction isolated at 131,000 × g; lane 7, inner membranes separated by sucrose gradient; lane 8, high-range molecular weight markers (Bio-Rad). (C) Immunoblot of crude extracts from E. coli cells transformed with pQE8072, using antibodies directed against purified soluble His6-CbbSRT189. Lane i, noninduced cells; lane ii, IPTG-induced cells; lane iii, purified His6-CbbSRT189. Each lane contained 30 μg of total protein.