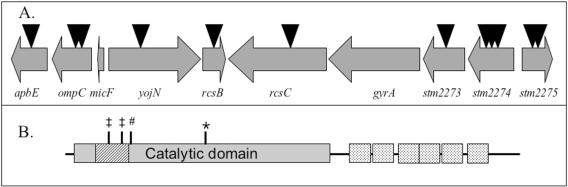
FIG. 2.
Physical map of the gyrA region and GyrA topology. (A) Insertions linked to the mutation causing loss of growth on succinate are shown as triangles. Based on the location of the insertions in the ORFs, the insertions were considered to cause null mutations. Double mutants containing an insertion and the succinate growth defect demonstrated that the causative lesion was not in any of these ORFs. (B) A schematic of the primary sequence of GyrA is shown (drawn to scale). Regions relevant to function and/or phenotype are noted as follows: #, active-site Y122; ‡, hot spots for Nalr mutations in Escherichia coli or S. enterica serovar Typhimurium; hatched box, quinolone resistance-determining area; dotted box, C-terminal chain; *, A271E (gyrA751).