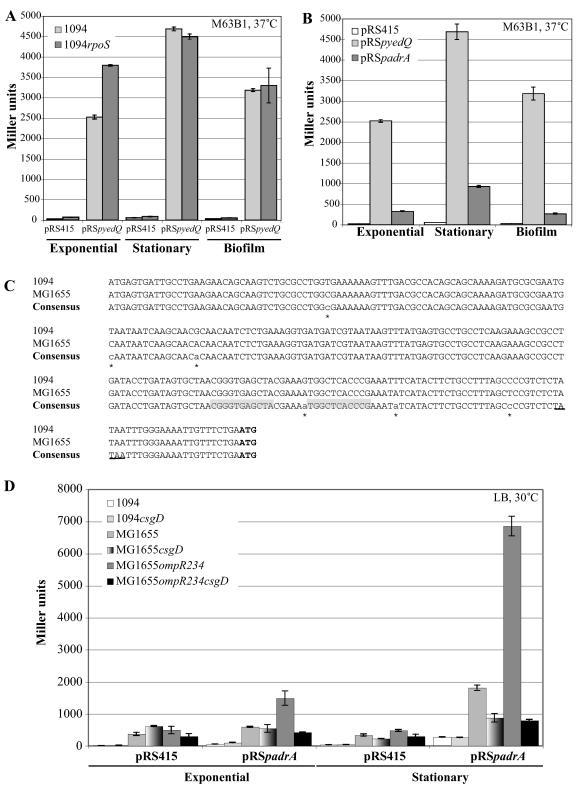
FIG. 4.
Transcriptional regulation of yedQ and adrA in strain 1094. (A) yedQ expression was studied in wild-type E. coli 1094 and the 1094rpoS mutant by measuring the β-galactosidase activity of a yedQ::lacZ fusion carried on the pRSpyedQ::lacZ plasmid. The cloning vector pRS415 was used as a negative control in both strains. Light-gray bars, β-galactosidase activity in 1094; dark-gray bars, β-galactosidase activity in 1094rpoS. The error bars represent standard errors of the means. (B) yedQ and adrA expression levels were compared in strain E. coli 1094 by measuring the β-galactosidase activities of a yedQ::lacZ and an adrA::lacZ fusion carried, respectively, on the pRSpyedQ::lacZ and pRSpadrA::lacZ plasmids. The cloning vector pRS415 was used as a negative control. White bars, pRS415 β-galactosidase activity; light-gray bars, pRSpyedQ::lacZ β-galactosidase activity; dark-gray bars, pRSpadrA::lacZ β-galactosidase activity. (C) Sequence alignment of the adrA promoters of E. coli strains 1094 and MG1655. The putative CsgD-binding sequences are shaded, and the −10 box is underlined on the consensus sequence. The sequence differences among E. coli strains are indicated by stars. The ATG start codon is in boldface letters. (D) adrA1094 expression was studied in the wild-type E. coli strains 1094, MG1655, and MG1655ompR234 (PHL818) and their respective csgD mutants by measuring the β-galactosidase activity of an adrA::lacZ fusion carried on the pRSpadrA::lacZ plasmid. The bar shades for β-galactosidase activities in the different strains are as indicated in the graph legend. All the measurements were done at least in triplicate at 37°C in M63B1 medium supplemented with 0.4% glucose (A and B) or at 30°C in LB medium (D).