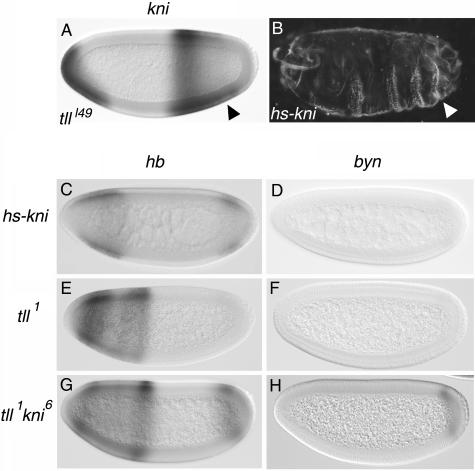
FIG. 5.
kni is partly responsible for the indirect effects of Tll on hb and byn. (A) Ectopic expression of kni in the posterior region of a tlll49 mutant embryo (arrowhead, compare with Fig. 3F). (B) Patterning defects induced by ectopic expression of kni under the control of a heat shock promoter; note the suppression of posterior terminal structures (arrowhead). (C and D) Expression patterns of hb (C) and byn (D) in heat-shocked hs-kni embryos; both genes appear significantly repressed (compare with Fig. 3I and L, respectively). (E to H) Expression of hb (E and G) and byn (F and H) in tll1 single-mutant (E and F) and tll1 kni6 double-mutant (G and H) embryos. Note that tll1 kni6 embryos exhibit enhanced posterior expression of hb and byn relative to tll1 embryos.