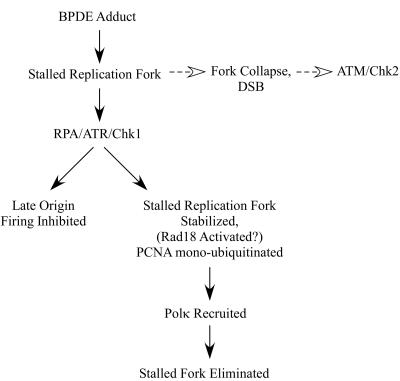
FIG. 10.
Hypothetical model describing the roles of Rad18 and Polκ in the BPDE-induced S-phase checkpoint. Replication forks stalled by BPDE-adducted DNA activate the ATR/Chk1 pathway. ATR/Chk1 signaling inhibits firing of late origins and also stabilizes stalled replication forks. Stabilization of a stalled fork could facilitate PCNA ubiquitination and recruitment of TLS polymerases indirectly. Alternatively, Chk1 signaling could stimulate PCNA ubiquitination directly, perhaps via Rad18 activation. Polκ is recruited to monoubiquitinated PCNA at the stalled fork. Polκ-mediated lesion bypass enables recovery of the stalled replication fork, and checkpoint signaling is attenuated. In the absence of Rad18/Polκ, stalled forks persist and eventually collapse, generating secondary forms of damage that activate ATM/Chk2.