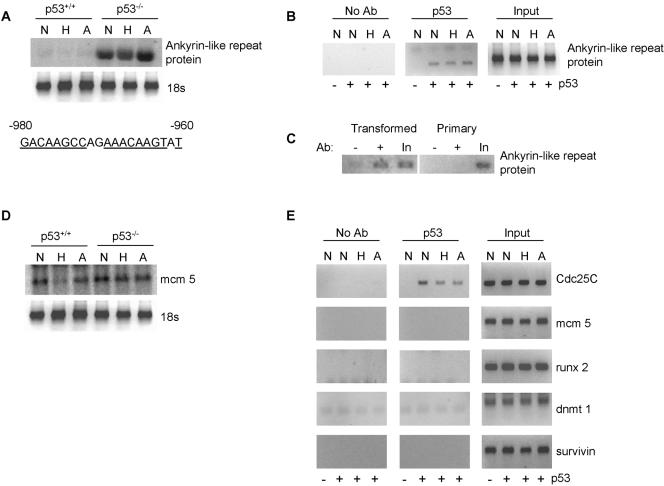
FIG. 5.
p53-dependent gene repression is not entirely mediated through association with the promoters of repressed genes. (A) MEFs (p53+/+ and p53−/−) were exposed to hypoxia or adriamycin for 8 h as described previously. The mRNA levels of Ankyrin-like repeat protein are shown. The 18s rRNA is shown as a loading control. The putative p53 response element identified in the Ankyrin-like repeat protein promoter is also shown. Those base pairs matching the canonical sequence for a p53 response element are underlined. (B) MEFs (p53+/+ and p53−/−) were treated as described for panel A. ChIP analysis was carried out using a p53 antibody (Ab), followed by PCR for the Ankyrin-like repeat protein promoter. (C) The binding of p53 to the Ankyrin-like repeat protein gene promoter was compared in primary and transformed MEFs. (D) MEFs (p53+/+ and p53−/−) were treated as described for panel A; the mRNA levels of mcm5 are shown. The 18s rRNA is shown as a loading control. (E) MEFs (p53+/+ and p53−/−) were treated as described for panel A. ChIP analysis was carried out using a p53 antibody, followed by PCR for the Cdc25C, mcm5, Runx 2, dnmt1, and survivin promoters.