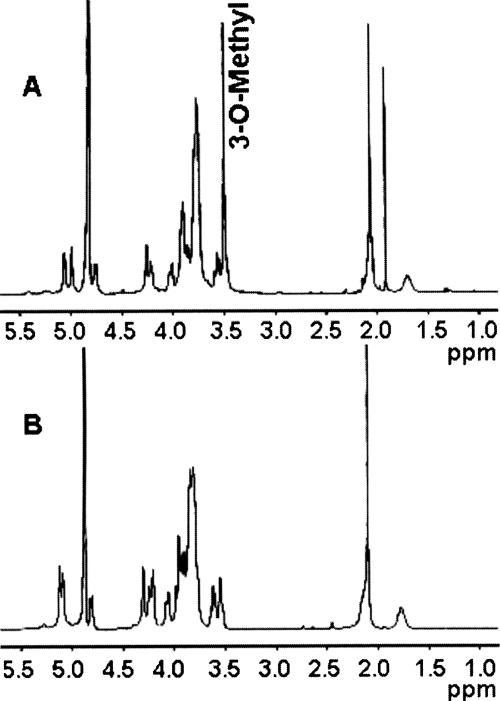
FIG. 7.
NMR analyses. (A) 1H NMR of C. jejuni 81-176 wild-type CPS (1% acetic acid treated) showing (i) the anomeric resonances at δ 5.06 for α-Gal, δ 4.99 for 3-O-Me-6-deoxy-α-altro-Hep, and δ 4.75 for β-GlcNAc, (ii) the methyl signal at δ 3.50 for 3-O-Me-6-deoxy-α-altro-Hep, (iii) the methyl resonance at δ 2.09 for 3-O-Me-6-deoxy-α-altro-Hep, and (iv) the deoxy resonance at δ 1.70 for 3-O-Me-6-deoxy-α-altro-Hep. (B) 1H NMR of C. jejuni 81-176 waaC CPS showing (i) the anomeric resonances at δ 5.12 for 6-deoxy-α-altro-Hep, δ 4.98 for α-Gal, and δ 4.75 for β-GlcNAc, (ii) the methyl signal at δ 2.09 for GlcNAc, and (iii) the deoxy resonance at δ 1.75 for GlcNAc. No 3-O-methyl signal (3-O-Me-6-deoxy-α-altro-Hep) was observed in the waaC CPS 1H NMR spectrum. Also of note, the α-anomeric signal of 6-deoxy-α-altro-Hep in the waaC CPS resonated at δ 5.12, whereas the α-anomeric signal of 3-O-Me-6-deoxy-α-altro-Hep in wild-type CPS resonated at δ 4.99. The peak at δ 1.9 in panel B represents contaminating sodium acetate. All the results described were assigned by 2D 1H-1H NMR spectroscopy (data not shown).