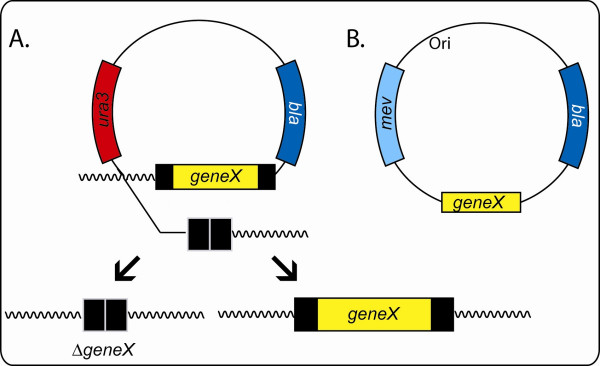
Figure 2.
Gene knockout strategies in Halobacterium sp. NRC-1. A. Nonessential genes. After a suicide vector containing a deletion of a gene of interest (geneX) is integrated into the Halobacterium Δura3 host strain by selection of uracil prototrophy (Ura+), plasmid excision is selected with 5-fluoroorotic acid resistance (Foar), resulting in either replacement with the deleted allele (ΔgeneX) (left) or restoration of the wild-type allele (right). For genes that are essential for cell viability, only wild-type gene alleles are recovered. B. Essential genes. A pseudo-complementation strategy is used where an autonomously replicating plasmid vector which contains the functional gene of interest, geneX, is introduced into the host strain, e.g. by selection for mevinolin resistance (Mevr). Knockout of the chromosomal copy may then be selected using selections described in part A.