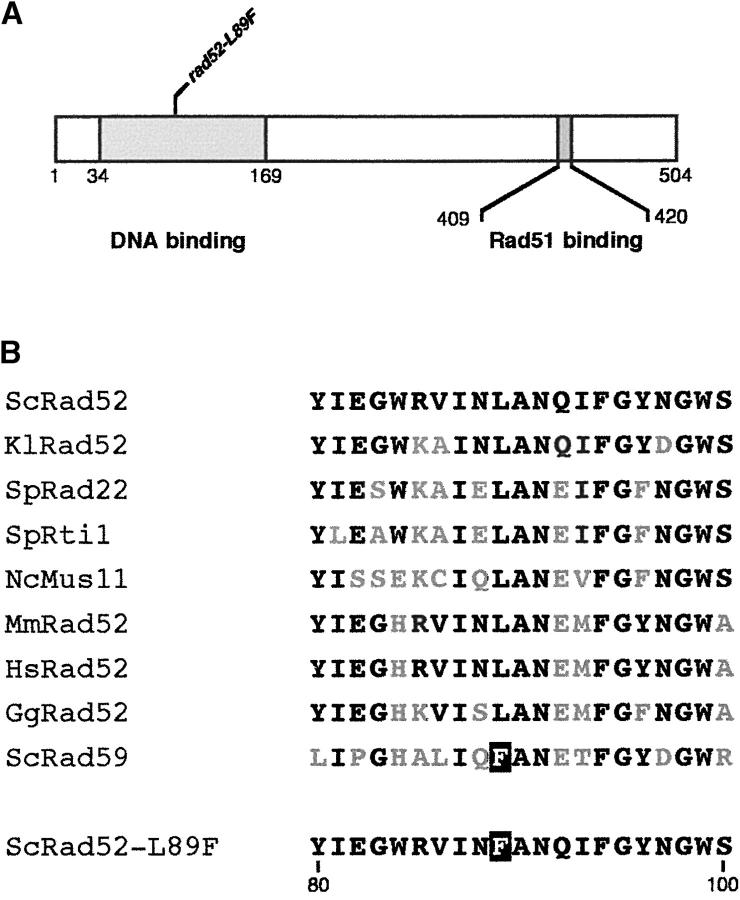
Figure 1.—
Primary structure of the Rad52-L89F protein. (A) Functional domains of Rad52 and localization of the rad52-L89F mutation. (B) Comparative alignment of Rad52 and Rad59 orthologs (Sc, S. cerevisiae; Kl, Kluyveromyces lactis; Sp, Schizosaccharomyces pombe; Nc, Neurospora crassa; Gg, chicken; Mm, mouse; Hs, human) and Rad52-L89F. Residues identical to those of ScRad52 are shown in black and the single substitution of Rad52-L89F is indicated as a solid box. The rad52-L89F mutant was obtained from the hyperrecombinant strain M137-11Ar51k (MATα ade2 can1-100 his3p::INV leu2 lys2-128α rad51Δ::KanMX4 spt6-140 trp1 ura3) by UV mutagenesis. Cells (50 μl) grown in YEPD to an OD660nm of 0.9 were diluted in 6 ml of water and poured into a glass petri dish for irradiation with 45 J/m2 of UV light (λ = 254 nm). After 5 hr of recovery in YEPD in the dark, cells were plated with the appropriate dilutions. Cell survival was 30% and 10,600 clones were screened for low His+ recombination.