Figure 5.—
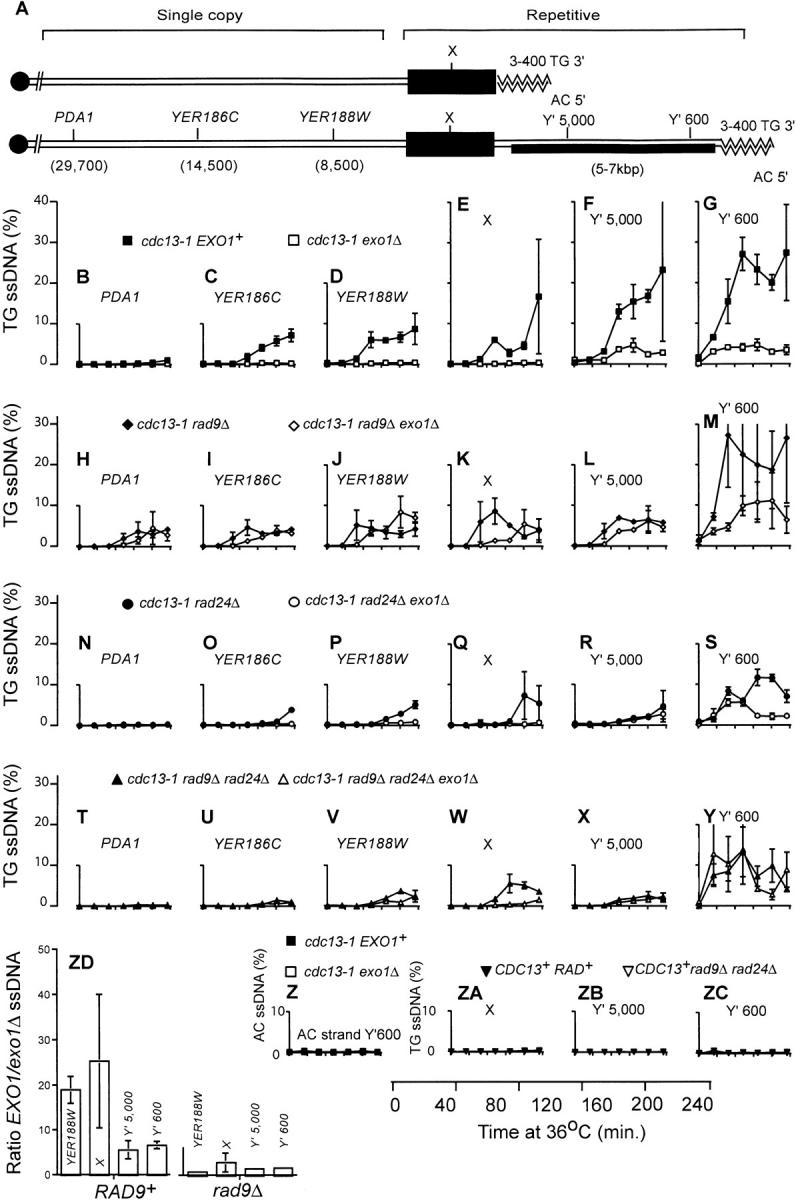
Exo1 is required to generate ssDNA in X and single-copy telomeric sequences in cdc13-1 mutants. (A) A schematic model of the two classes of telomere in budding yeast. One class contains an X repeat, but no Y′ repeats, and the other class contains one or more Y′ repeats, in addition to the X repeats. The bottom half of A is a representation of the right telomere of the sequenced chromosome V present in the Saccharomyces Genome Database. It comprises a 3- to 400-bp TG/AC repeat, a Y′ repeat, a 374-bp X repeat, and the YER188W, YER186C, and PDA1 single-copy loci. Using primers and probes directed to repetitive and single-copy loci we were able to detect the appearance of ssDNA in repetitive elements (at numerous telomeres, including 5R) and also specifically 8500, 14,500 and 29,700 bp from the right telomere of chromosome V. Yeast strains were released from G1 arrest to 36°, and the amount of ssDNA was measured by quantitative amplification of ssDNA (QAOS; Booth et al. 2001). In most cases the data points indicate the average amount of ssDNA measured in two independent strains of identical genotype, with error bars indicating the difference observed between the two strains. When the amount of ssDNA in a genotype had been previously measured (Booth et al. 2001), a single new experiment was performed with error bars representing the standard error of the mean of three independent measurements. In cases where a single strain of a particular genotype was identified, two independent synchronous cultures of that strain were performed and the difference in values between the two experiments is indicated by the error bars. (B–G) Yeast stains containing cdc13-1 (DLY1468 and DLY1469, solid squares) and cdc13-1 exo1Δ (DLY1431 and DLY1432, open squares) mutations. (H–M) Yeast strains containing cdc13-1 rad9Δ (DLY1470 and DLY1471, solid diamonds) and cdc13-1 rad9Δ exo1Δ (DLY1433 and DLY1476, open diamonds) mutations.(N–S) Yeast strains containing cdc13-1 rad24Δ (DLY1472, single experiment, solid circles) and cdc13-1 rad24Δ exo1Δ (DLY1434, duplicate experiments, open circles) mutations.(T–Y) Yeast strains containing cdc13-1 rad9 rad24Δ (DLY1474, single experiment, solid triangles) and cdc13-1rad9Δ rad24Δ exo1Δ (DLY1435 and 1477, open triangles) mutations. (Z) Yeast strains and symbols are as in G, and ssDNA was measured on the AC strand. (ZA–ZC) Yeast strains containing CDC13+ cdc15-2 RAD+ (DLY 1363, single experiment, solid downward-pointing triangles) and CDC13+ rad9Δ rad24Δ cdc15-2 (DLY1414, single experiment, open downward-pointing triangle) mutations. (ZD) A histogram showing the ratio between the amount of ssDNA observed at four telomeric loci in cdc13-1 EXO1+ vs. cdc13-1 exo1Δ strains and corresponding rad9Δ strains. Ratios shown are average ratios of ssDNA in EXO1+ vs. exo1Δ strains at 120-, 160-, 200-, and 240-min time points. The ratios were determined from the data plotted in D–G and J–M. The error bars show the standard error of the mean.
