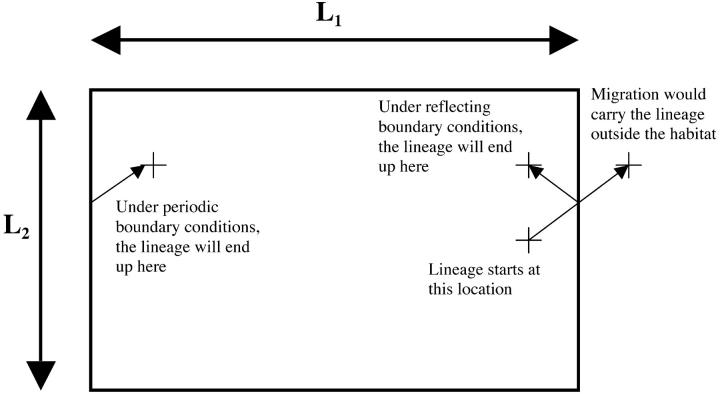
Figure 1.—
Habitat geometry and boundary conditions. The two-dimensional habitat considered in this article is a rectangle of dimensions L1 × L2, where L1 ≥ L2. Two different treatments of the boundaries are considered. In the “rectangular” model, reflecting boundary conditions are assumed, and a lineage exiting the habitat reenters on the same side. In the “toroidal” model, periodic boundary conditions are assumed, and a lineage reaching the boundary reenters the habitat from the opposite side.