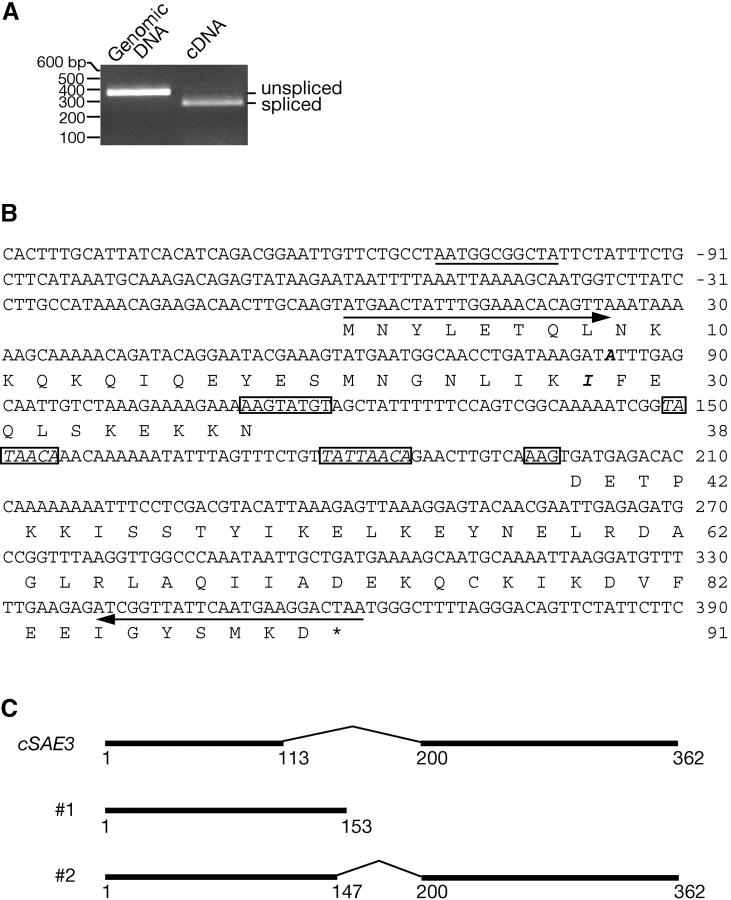
Figure 3.—
The SAE3 gene has an intron. (A) Genomic and cDNA derived from meiotic mRNA were amplified by PCR with primers and analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis. (B) DNA sequence and encoded amino acid sequence of SAE3. Consensus splicing signals are boxed. Italicized boxed sequences indicate potential branchpoint sequences (see text). A URS1 consensus sequence is underlined. Primers used for PCR amplification are shown with arrows. Compared to the sequence of strain S288c published in the Saccharomyces Genome Database (http://www.yeastgenome.org), the SK1 strain from which SAE3 cDNA was derived has a polymorphism at the 83rd nucleotide—A (italicized in boldface type) instead of G. The single nucleotide substitution changes the 28th amino acid from M to I (italicized in boldface type). Numbering starts at the first nucleotide of the first codon for the DNA sequence and the first amino acid for the amino acid sequence. (C) Structure of SAE3 ORFs. The structure of the cDNA found in this study is shown on top. Structure 1 was proposed by McKee and Kleckner (1997). Structure 2 was proposed by Akamatsu et al. (2003).