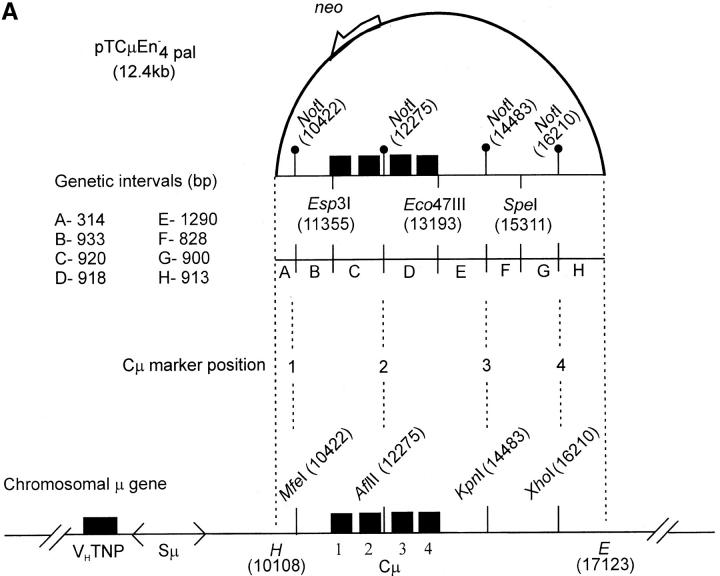
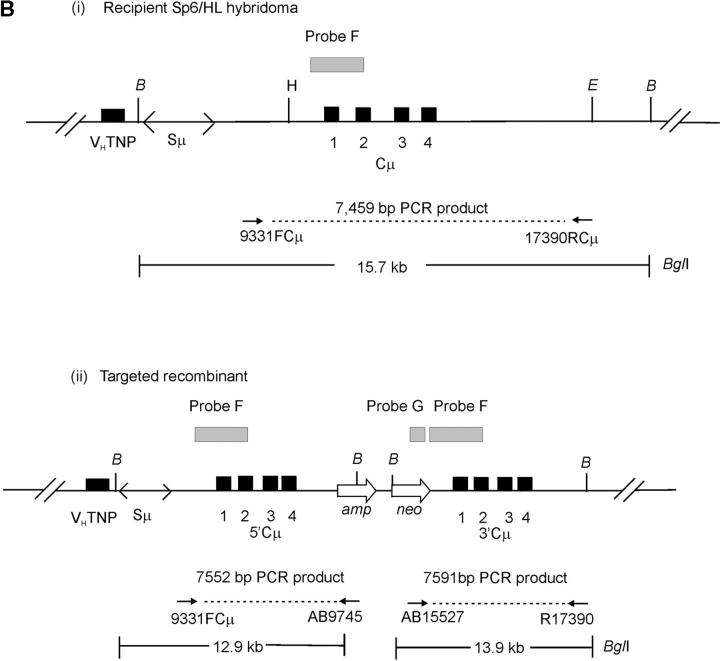
Figure 3.—
Vector and chromosomal DNA structures. (A) Enhancer-trap gene-targeting vector. The vector pTCμEn−4pal contains a 7016-bp segment of homology to the Cμ region of the mouse chromosomal immunoglobulin μ-gene inserted into a derivative of pSV2neo in which the SV40 early region enhancer has been deleted. The vector-borne Cμ region of homology is interrupted at regular intervals by insertion of a 30-bp palindrome sequence containing a diagnostic NotI restriction enzyme site (Li et al. 1999), which replaces endogenous MfeI, AflII, KpnI, and XhoI sites. Unique Esp3I, Eco47III, and SpeI recognition sequences within the vector-borne Cμ region permit introduction of the recombination-initiating DSB. As the genetic intervals (A–H) indicate, flanking palindrome markers reside approximately equidistantly from each DSB site. The numbering system used to denote restriction enzyme sites is based on the genomic wild-type μ gene sequence (Goldberg et al. 1981; Bilofsky et al. 1986). (B) Chromosomal immunoglobulin μ-gene structures. (i and ii) The structures of the haploid chromosomal μ-gene in the recipient Sp6/HL and targeted recombinant hybridoma cell lines, respectively. Diagnostic bands that can be detected through PCR and Southern analysis are indicated. DNA probe fragments used in Southern analysis include probe F, an 870-bp XbaI/BamHI fragment, and probe G, a 762-bp PvuII fragment from the neo gene of pSV2neo. VHTNP, TNP-specific chromosomal immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region; Sμ, immunoglobulin μ-gene switch region; Cμ, four exons composing the immunoglobulin μ-gene constant region; B, BglI; E, EcoRI; H, HindIII. The diagrams are not drawn to scale.