Figure 4.—
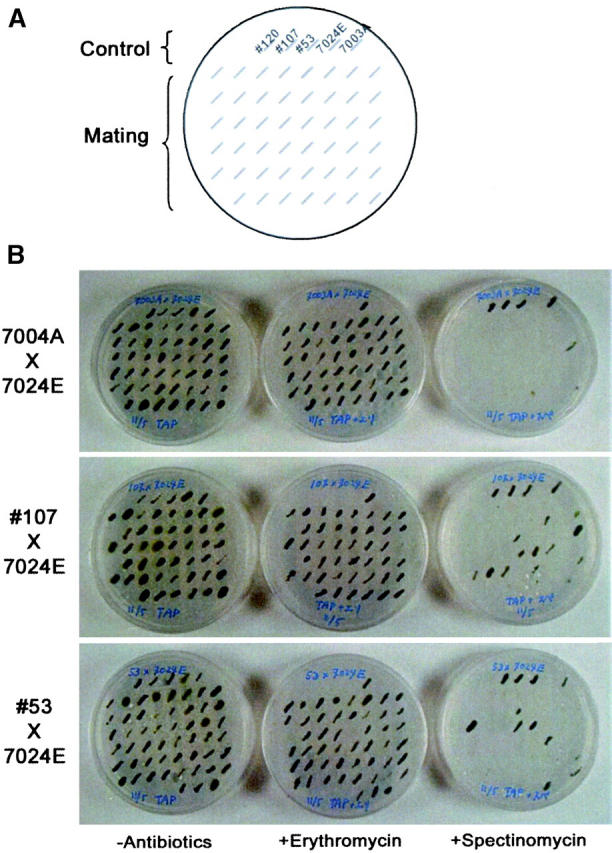
Effects of DMT1 on transmission of chloroplast genes. Each cross was performed using strains with chloroplast antibiotic markers: erythromycin and spectinomycin resistance for mt+ and mt−, respectively. Zygote colonies with serial numbers as indicated were plated; incubated for 4–10 days; and scored for mt+ uniparental colonies by resistance against erythromycin, for biparental colonies by spectinomycin and erythromycin resistance, and for mt− uniparental colonies by spectinomycin resistance. (A) The positions of strains loaded on the plate below. The control lane illustrates colonies from left to right of transgenic lines 120, 107, and 53 and wild-type lines 7024E (mt+) and 7003A (mt−), respectively. The mating lane shows the position of colonies from each crossing. (B) Crossing results. Crossings between 7024E (mt+) and 7003A (wild-type mt−), between 7024E (mt+) and 107 (transgenic mt−), and between 7024E (mt+) and 53 (transgenic mt−) are shown in the top, middle, and bottom, respectively. Culture medium contained no antibiotics (left), erythromycin (middle), or spectinomycin (right) as indicated at the bottom.
