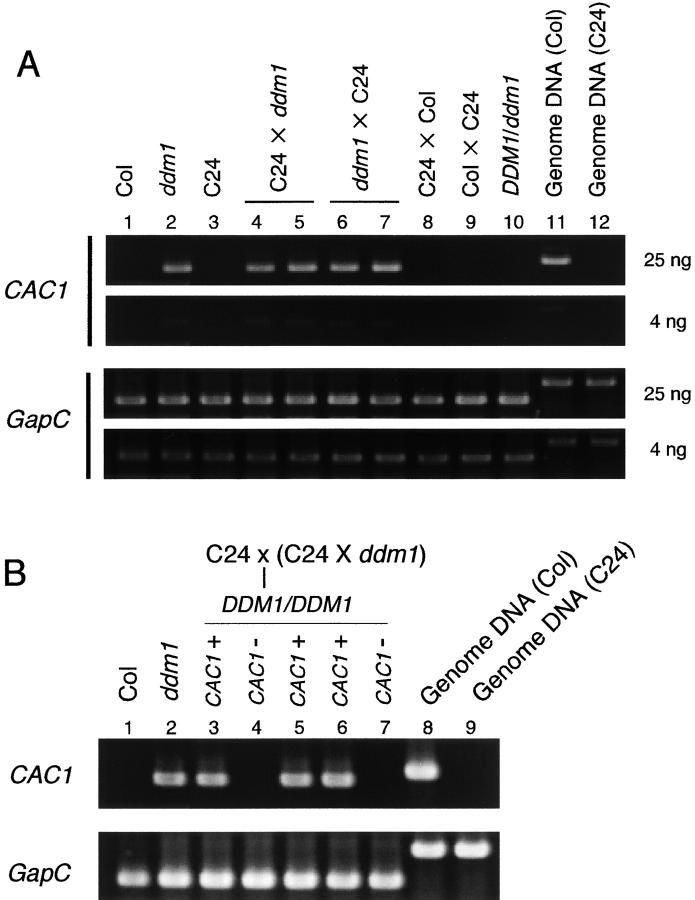
Figure 1.—
(A) Transcription of ddm1-derived CACTA1 after crosses to wild-type plants. Semiquantitative RT-PCR reactions corresponding to 25 ng and 4 ng of input total RNA are shown for each plant. C24 and Col represent wild-type (DDM1/DDM1) plants in those ecotypes. The DDM1/ddm1 heterozygote in lane 10 was derived from a ddm1/ddm1 Columbia plant, which was backcrossed six times to the wild-type Columbia plant in the heterozygous state (Kakutani et al. 1999). (B) Transcription of ddm1-derived CACTA1 after two successive backcrosses to C24 wild-type plants. Because C24 does not have CACTA1, plants with and without CACTA1 segregate after the second backcross (lanes 3, 5, and 6, and lanes 4 and 7, respectively). The plants in lanes 3 and 4 and lanes 5–7 are siblings. The constitutively expressed GapC gene was used as a control. Length of the predicted PCR product: CACTA1, 0.64 kb for cDNA and 0.72 kb for genomic DNA; GapC, 0.54 kb for cDNA and 0.82 kb for genomic DNA.