Figure 4.—
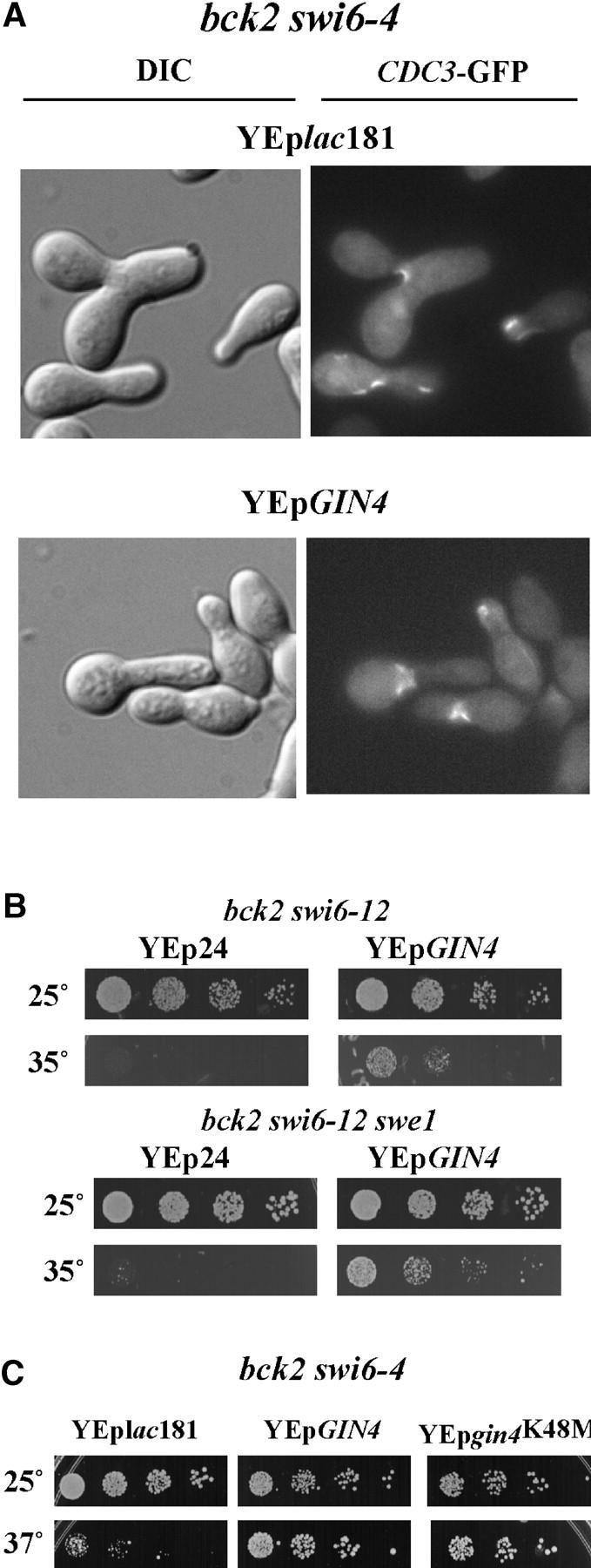
Suppression of bck2Δ swi6-ts by GIN4. (A) Morphogenetic and septin ring defects in bck2Δ swi6-ts mutants with and without multicopy GIN4. bck2 swi6-4 strains carrying either control plasmid (YEplac181) or YEpGIN4 were transformed with YCpCDC3-GFP. Cells were grown to log phase at permissive temperature and then shifted to 35° for a time course; the 10-hr point is shown here. For microscopic analysis, cells were fixed in methanol at −70°. DIC and fluorescence microscopy were performed using an Eclipse E800 microscope with a ×100 objective. (B) Suppression by GIN4 is not dependent upon SWE1. bck2 swi6-12 cells (top) and bck2 swi6-12 swe1 (bottom) were transformed with a control plasmid (Yep24) or YEpGIN4. Spotting assays were done as described in Figure 1. (C) Suppression by GIN4 is not dependent upon a functional protein kinase domain. bck2 swi6-4 cells were transformed with a control plasmid (YEplac181), YEpGIN4, or YEpgin4K48M. YEpgin4K48M harbors a mutation that renders GIN4 kinase inactive (Longtine et al. 1998). Cell growth and spotting assays were performed as described above.
