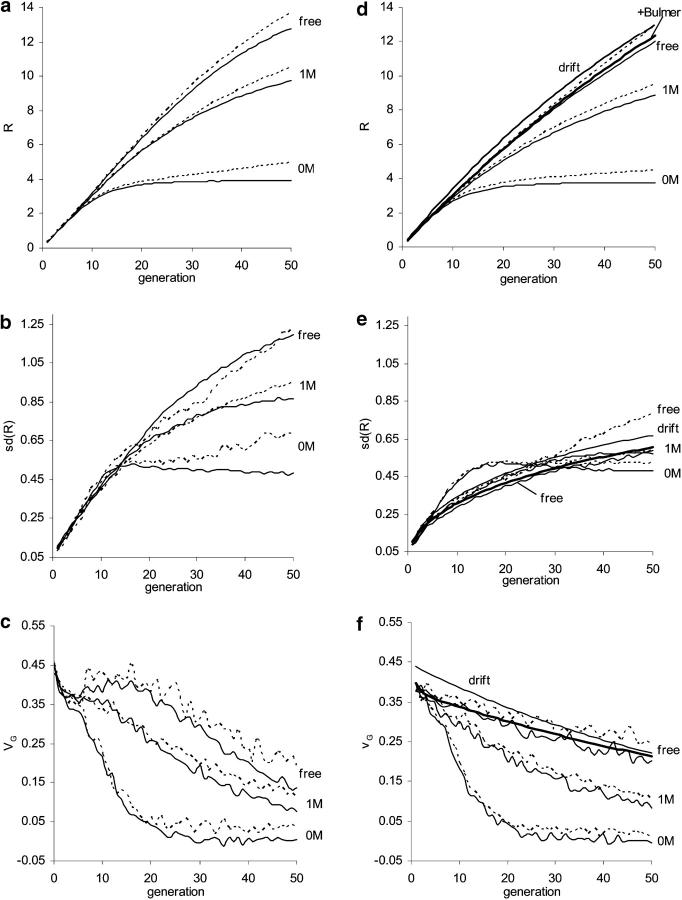
Figure 5.—
Influence of new mutation and comparison between predictions from the natural selection model (left) and from the infinitesimal model and modification of it (right). For the natural selection model (a–c), effects of new mutations were sampled from a reflected gamma 1/4 distribution with mutation rate λ = 0.3 per generation per haploid genome. For the infinitesimal model (d–f), effects of mutations within each locus are sampled from a normal distribution of mean 0 and variance VG0/(2 × 5740) with a rate 2 × 5740 × (VM/VG0) per generation per genome, where VM = 10−3VE and 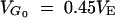 . Artificial selection is as in Figure 2 (N = 40, 40% selected). Three linkage patterns are considered: each chromosome of map length 0, 1, and ∞ M. Solid lines represent predictions without new mutations while dashed lines show prediction with contribution from new mutation. For comparison, d–f also show the Robertsonian formulas, where genetic drift alone affects frequencies (thin solid lines) and also predictions with incorporation of linkage disequilibrium due to the Bulmer effect (thick solid lines).
. Artificial selection is as in Figure 2 (N = 40, 40% selected). Three linkage patterns are considered: each chromosome of map length 0, 1, and ∞ M. Solid lines represent predictions without new mutations while dashed lines show prediction with contribution from new mutation. For comparison, d–f also show the Robertsonian formulas, where genetic drift alone affects frequencies (thin solid lines) and also predictions with incorporation of linkage disequilibrium due to the Bulmer effect (thick solid lines).