Figure 5.—
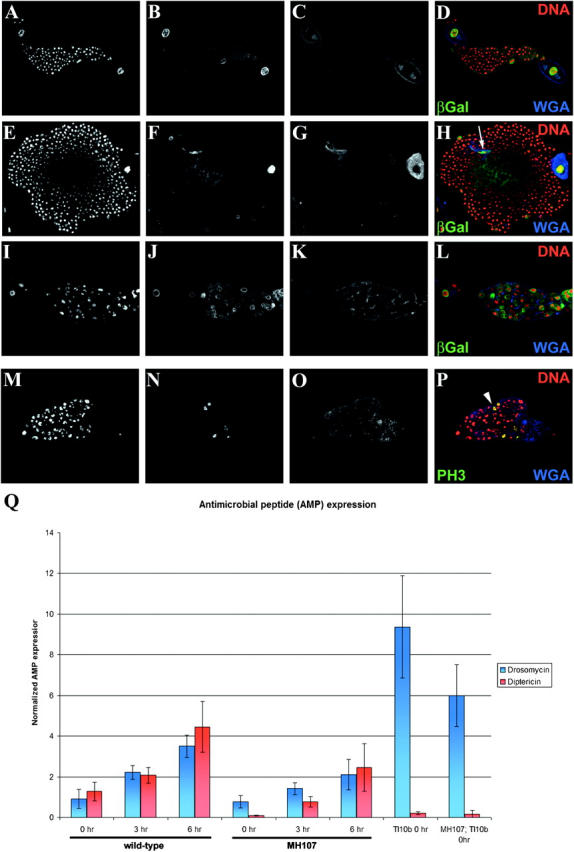
Toll10b, Dm-Myb−/− double-mutant secondary lymph gland hemocytes fail to overproliferate and abnormally differentiate into lamellocytes. (A–D) Control with lamellocyte enhancer-trap (y,w67; msnlacZ). (E–H) Toll10b mutant with lamellocyte enhancer-trap (Tl10b/msnlacZ). WGA+ and enhancer-trap (msnlacZ)-positive lamellocytes are indicated by the arrow (H). (I–L) Dm-Myb mutant with lamellocyte enhancer-trap (MH107; msnlacZ). (M–P) Toll10b, Dm-Myb−/− double mutant (MH107; Tl10b). Increased PH3-labeled hemocytes are indicated with an arrowhead (P) in the Toll10b, Dm-Myb−/− double mutant. Third instar secondary larval lymph gland lobes were stained with PI (A, E, I, and M), wheat germ agglutinin (WGA; C, G, K, and O) and anti-β-gal antibody (B, F, and J) or anti-PH3 antibody (N). (Q) Drosomycin and Diptericin are expressed in Dm-Myb mutant larvae in response to bacterial challenge. A needle inoculated with E. coli and M. luteus was used to prick late third instar larvae and the induction of Drosomycin (blue bars) and Diptericin (red bars) expression was measured by real-time RT-PCR analysis. Drosomycin and Diptericin transcript levels were normalized to the expression of the ribosomal protein 15a transcript in each sample. (Columns 1–3) Control (yw67) Drosomycin and Diptericin expression over 0, 3, and 6 hr of bacterial challenge. (Columns 4–6) Dm-Myb mutant (MH107) Drosomycin and Diptericin expression over 0, 3, and 6 hr of bacterial challenge. (Column 7) Unchallenged Toll10b dominant mutant Drosomycin and Diptericin expression. (Column 8) Unchallenged Toll10b, Dm-Myb−/− double-mutant (MH107; Tl10b) Drosomycin and Diptericin expression.
