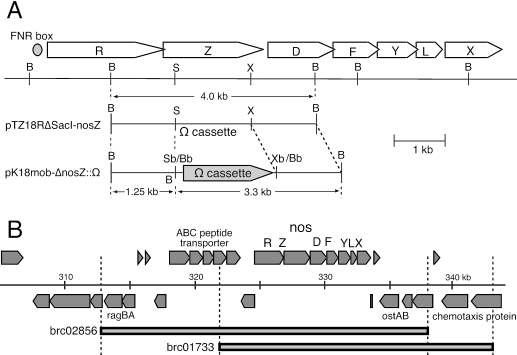
FIG. 1.
Construction of a nosZ mutant (A) and complementation cosmid inserts (B) of Bradyrhizobium japonicum USDA110. (A) Cloned fragments in pTZ18RΔSacI-nosZ and pK18mob-ΔnosZ::Ω are shown alongside the physical map of the nos gene cluster of B. japonicum USDA110. B, BamHI; S, SacI; X, XhoI; Sb, SacI blunt end; Bb, BamHI blunt end; Xb, XhoI blunt end. During blunt-end ligation, the Sb/Bb site produced a BamHI site in pK18mob-ΔnosZ::Ω. Upstream of nosR lies a consensus sequence of an FNR box (TTGAT-N4-ATCAA) (50). The cloned 4-kb DNA fragment containing the nosZ gene in pTZ18R-nosZ was reconnected to pTZ18RΔSacI, which was produced by blunting of the SacI site of pTZ18R, and pTZ18RΔSacI-nosZ was generated. The Ω cassette, which was excised from pHP45Ω (40), digested with BamHI, and blunt ended, was inserted into the blunt-ended SacI and XhoI sites of pTZ18RΔSacI-nosZ to generate pTZ18RΔSacI-nosZ::Ω. Finally, the fragment containing the nosZ and Ω cassette fusion was inserted between the SmaI and XbaI sites of pK18mob to generate pK18mob-nosZ::Ω. (B) Positions covered by two cosmid inserts, brc02856 and brc01733 (Table 1), in the genome of B. japonicum USDA110 (http://www.kazusa.or.jp/rhizobase/) (23).