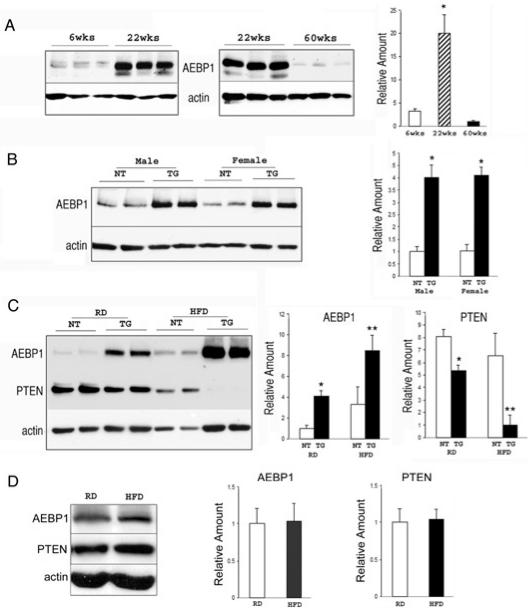
Figure 2.
Age and diet modulate AEBP1 expression in a sex-specific manner. (A) Expression of AEBP1 was examined by immunoblotting with anti-AEBP1 antibody in female mice at 6 weeks (n = 4), 22 weeks (n = 4), and 60 weeks (n = 3) of age. Actin is used as a loading control. The average values of AEBP1 expression in WAT at different ages are represented as mean ± SD. *P = 0.0002 (between 6 and 22 weeks); *P = 0.0005 (between 22 and 60 weeks). (B) Expression of AEBP1 was examined by immunoblotting with anti-AEBP1 antibody in regular diet–fed NT (male, n = 5; female, n = 6) and TG (male, n = 5; female, n = 7) mice at 32 weeks. Actin is used as a loading control. The average values of AEBP1 expression in WAT from NT and TG mice are represented as mean ± SD. *P < 0.0001 compared with NT mice. (C) Expression of AEBP1 and PTEN were examined by immunoblotting with anti-AEBP1 or anti-PTEN antibody in NT (RD, n = 6; HFD, n = 6) and TG (RD, n = 7; HFD, n = 6) females (32 weeks) that were fed on either regular diet (RD) or HFD for 29 weeks. Actin is used as a loading control. The average values of AEBP1 and PTEN expression in WAT from NT and TG mice are represented as mean ± SD. *P < 0.0001 compared with RD-fed NT mice, **P ≤ 0.0002 compared with HFD-fed NT mice. (D) Expression of AEBP1 and PTEN were examined by immunoblotting with anti-AEBP1 or anti-PTEN antibody in NT males (30 to 32 weeks) that were fed on either RD (n = 5) or HFD (n = 5) for 20 to 29 weeks. Actin was used as a loading control. The average values of AEBP1 and PTEN expression in WAT from NT mice are represented as mean ± SD.