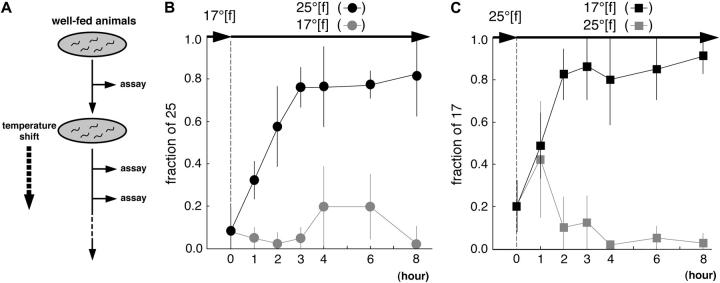
Figure 2.—
The memory formation to a new temperature takes a few hours for well-fed animals in the radial temperature-gradient assay. (A) Experimental procedure for cultivation-temperature-shifted assay at the well-fed state. The solid ellipsoid indicates a conditioning plate with food. The thermotaxis behavior of naive and temperature-shifted animals was assayed at designated times after cultivation-temperature shift. (B) Cultivation temperature was shifted at the well-fed state from 17° to 25°. Animals temperature shifted after 1 hr had significant differences from naive animals (P < 0.01), and animals temperature-shifted after >2 hr had significant differences (P < 0.0001). (C) Cultivation temperature was shifted at the well-fed state from 25° to 17°. Animals temperature shifted after 1 hr had significant differences from naive animals (P < 0.01), and animals temperature shifted after >2 hr had significant differences (P < 0.0001). Thermotaxis was evaluated using “fraction of 17,” which includes the class “17,” and “fraction of 25,” which includes the class “25.” Top arrows indicate cultivation temperature and feeding state; “f” indicates cultivation with food. About 20 animals were examined at each time point in four trials. Error bar indicates SD.