TABLE 2.
Variogram parameters forLobaria pulmonaria
| Variogram modeling
|
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diversity measure | Weighting | 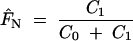 |
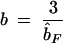 |
C = C0 + C1 | Conventional estimation: V̂, Ĥ, D̂ |
| Molecular variance V | All samples | 0.93 | 121.5 | 25.1 | 24.3 |
| Weighted for clones | 0.66 | 58.2 | 25.7 | 25.5 | |
| Gene diversity H | All samples | 0.87 | 135.9 | 0.67 | 0.64 |
| Weighted for clones | 0.55 | 69.3 | 0.68 | 0.68 | |
| Genotypic diversity D | All samples | 0.71 | 106.5 | 1.00 | 0.98 |
| WSW–ENE | — | 158.7 | 1.00 | — | |
| WNW–ESE | — | 77.7 | 1.00 | — | |
| SSW–NNE | — | 89.7 | 0.99 | — | |
| NNW–SSE | — | 110.7 | 1.00 | — | |
Estimated parameters of the exponential variogram model were fitted to the variograms of molecular variance and gene diversity for a population of Lobaria pulmonaria (N = 461) assessed with six microsatellite markers, with and without accounting for recurrent genotypes, and for genotypic diversity (clonal structure), with and without accounting for compass direction. The relatedness between immediate neighbors, FN, is estimated from the autocorrelation of the first distance class of thalli taken from the same tree. The range parameter b denotes the distance at which the curve reaches 95% of the sill and provides an estimate of the extent of spatial genetic structure. The total sill C estimates the population diversity (molecular variance, gene diversity, or genotypic diversity) accounting for spatial autocorrelation, whereas the conventional estimators V̂, Ĥ, and D̂ do not account for autocorrelation and are, therefore, susceptible to bias.
