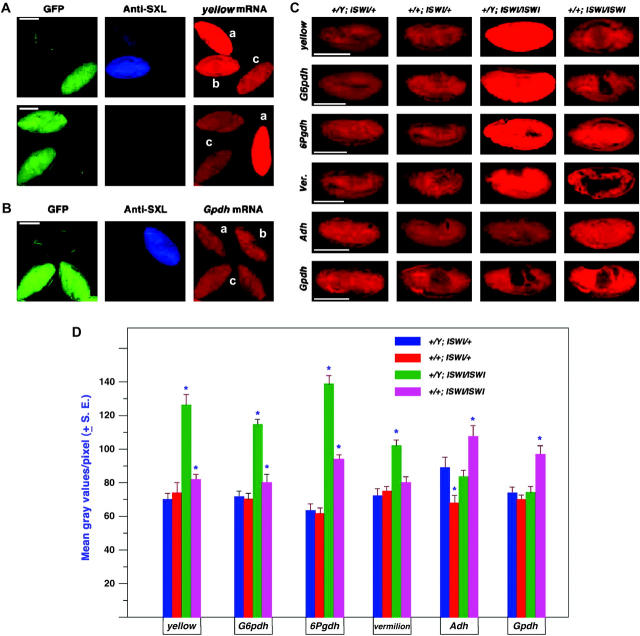
Figure 8.—
Gene expression in the ISWI segregating population of embryos. Embryos were collected from a cross of w−/Y; CyO, GFP/ISWI1 × w−/w−; CyO GFP/ISWI2. Genotypes were classified on the basis of antibody labeling against SXL to determine sex and GFP excitation to determine the ISWI constitution. (A) Mixed stage embryos in the same field probed for the expression of the X-linked yellow gene. a, male ISWI mutant homozygote; b, female mutant homozygote; c, normal male. (B) Mixed stage embryos in the same field probed for the autosomal gene, α-Gpdh. a, male mutant homozygote; b, normal female; c, normal male. (C) Representative embryos at approximately stage 13 for four X-linked genes (y, G6pdh, 6Pgdh, and v) and two autosomal genes (Adh and α-Gpdh). The white gene expression was not tested because the X chromosome in these stocks carries a mutant allele. (D) Histogram of the mean gray values of embryos at approximately stage 13 from the segregating ISWI population. A range of 10 to 20 embryos were analyzed for each mean. An asterisk denotes those means that are significantly different from the normal genotype of the same sex.