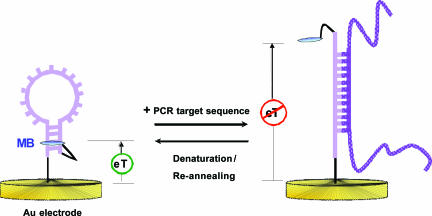
Fig. 1.
An E-DNA-based PCR sensor fabricated by self-assembly of a MB-labeled DNA probe on a gold electrode surface. In the absence of a target, the stem-loop structure holds the MB tag in proximity to the electrode surface, thus enabling efficient electron transfer. Upon hybridization with the target PCR amplicon, a large change in the reduction peak current of MB is observed. A room temperature distilled water wash is sufficient to disrupt hybridization and reset this reagentless, electrochemical sensor.